What is Kubernetes ☸?
- In simpler words Kubernetes is an opensource container orchestration tool, for automating, scaling and deployment and management of containerized applications.
- Kubernetes is also represented as k8S . So here 8 represents the simple quantity of letters in between the starting and ending collateral.
- Kubernetes was developed by Google in 2014.
- Kubernetes helps us to manage containerized applications in different deployment environments like physical, virtual, hybrid ,cloud environments.

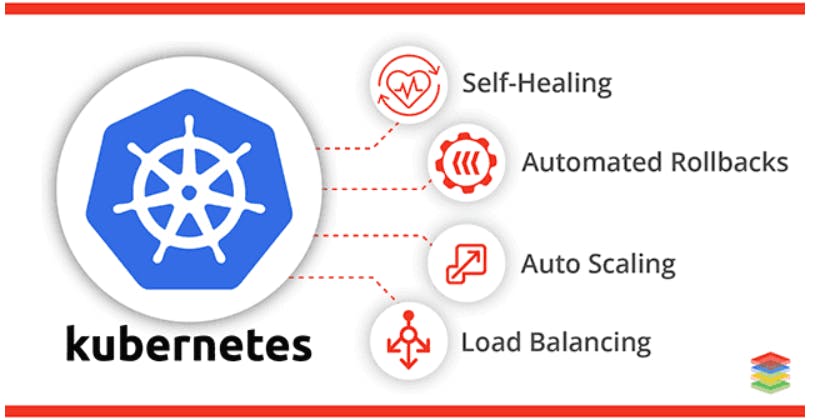
Kubernetes Features 🏆
- In the recent years, due to the increase in usage of containers the demand for a proper way of managing those hundreds of containers has came into existence.
1) High availability or no down time.
2) Auto-scaling of the deployed applications.
3) Automatic replacement of the failed containers.
4) Distribution of load across many servers and maintaining a balance.
5) Monitoring and health check of the containers.
6) Automated rollbacks and rollouts.
7) Self-healing
Kubernetes Components ⚡
Kubernetes has tons of components, but we mostly work with a quite a bit of it.
Kubernetes components helps us in deploying the applications.
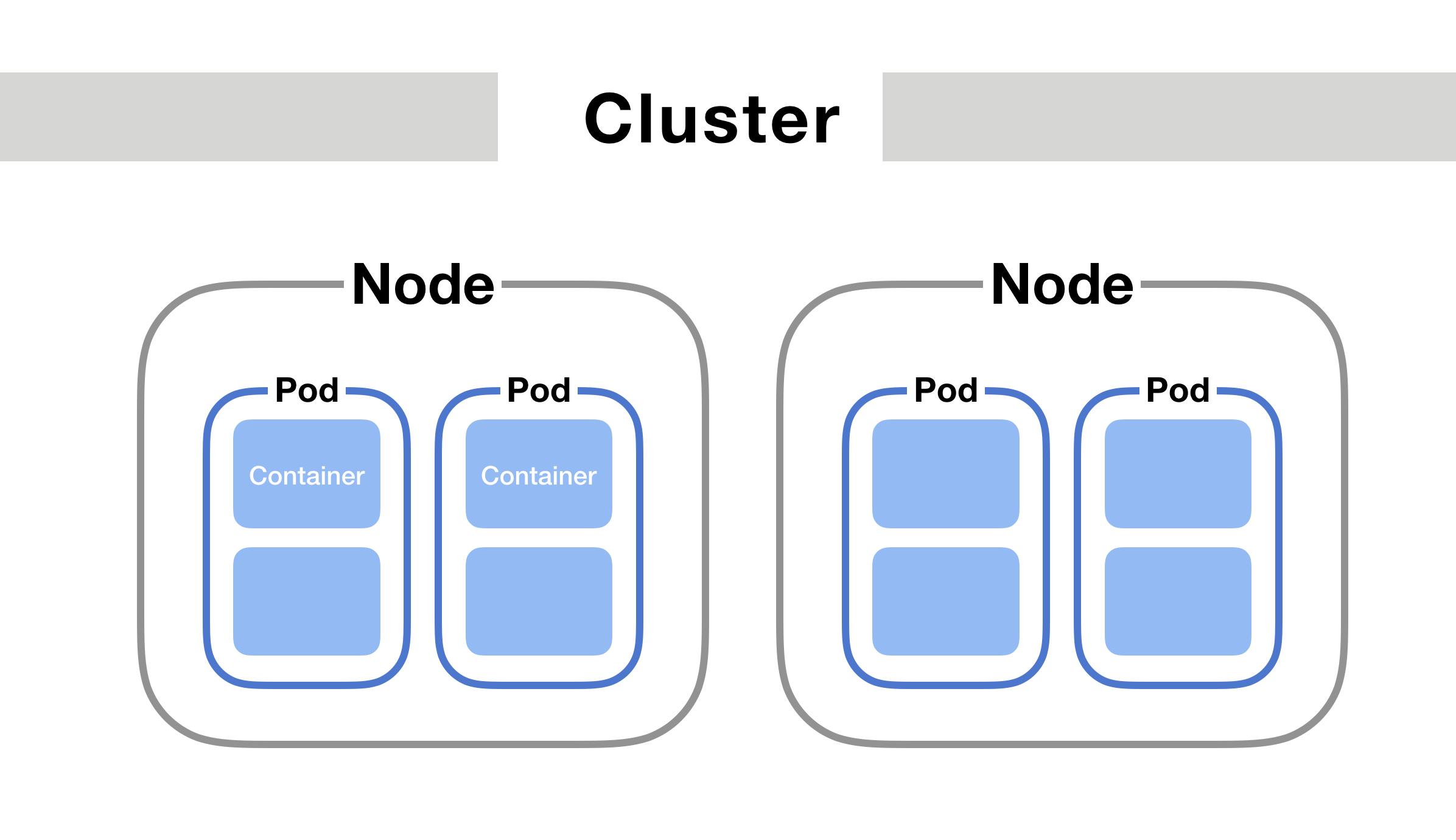
1) Node and Pod :
- Kubernetes consists of two types of node master node and worker node. A node is a simple server or a virtual machine
The smallest unit of kubernetes is called pod.
Pod creates a running environment or a layer on the top of the container.
Each pod has its own IP address and each pod communicate with each other through IP address.
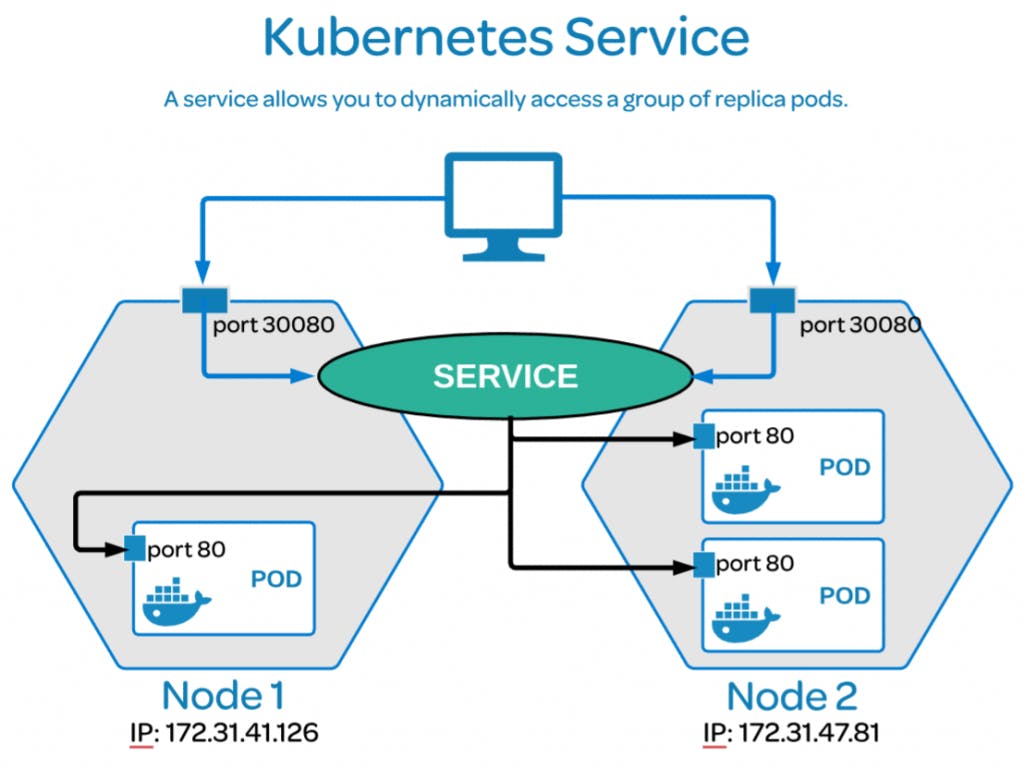
2) Service :
It is basically a permanent IP address which is attached to the each pod.
The best thing about the service is even if the pod dies, the service and its IP address will not be get affected and still works.
Service is also like a load balancer.
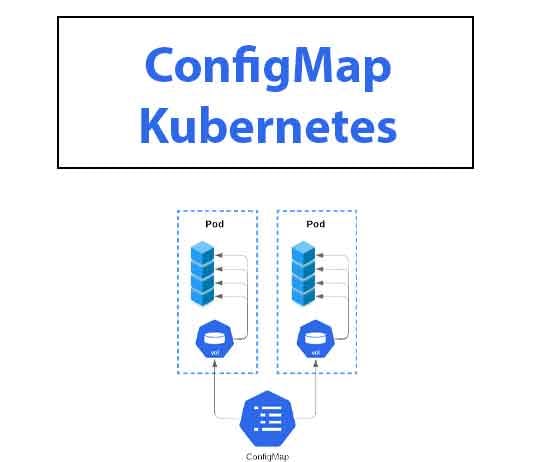
3) Config Map and Secret :
Config Map usually contains the configuration data like URL's of the database and some other services which we usually use in kubernetes.
The secret is just like config map but the main difference between config map and secret is that's used to store the secret data credentials in base64 encoded.
4) Volumes :
When we restart the pod the data which is stored gets lost which is a problematic, to solve this problem there is an another kubernetes component called Volumes.
Volumes attaches a physically storage on a hard drive to the pod and it could be on the remote, outside of the k8s cluster.
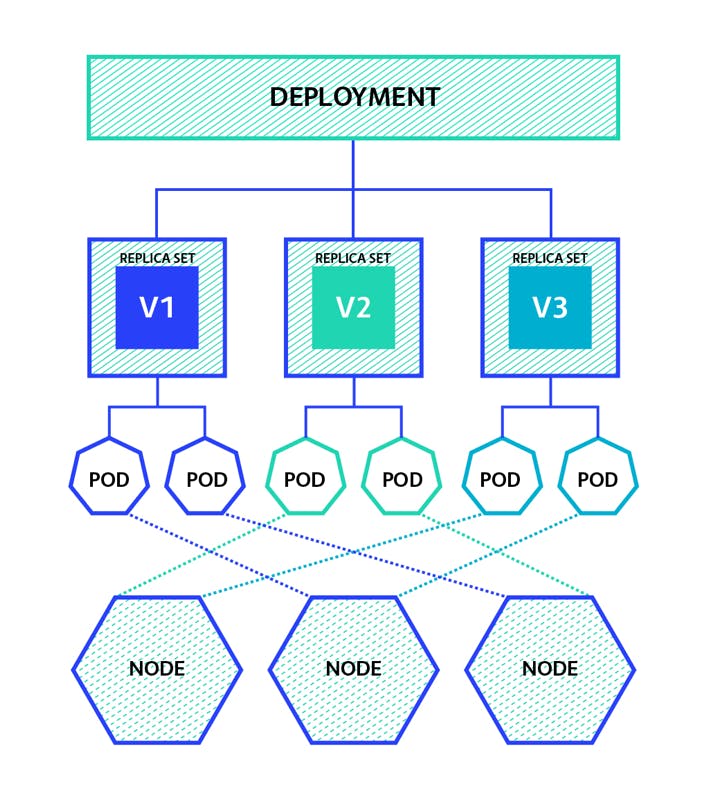
5) Deployment :
At any moment of time It acts like a blue print for the pods and we practically work with the deployments to create replicas which is used to scale up or down the number of replicas of the pods.
Deployments are another layer of abstraction on the top of pods which makes us more convenient to work with the pods.
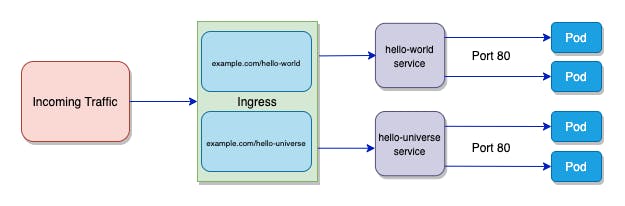
6) Ingress :
Ingress is used to route the traffic into the cluster.
It also allows access to the kubernetes services from outside the cluster.
After having sneak peek into the kubernetes components lets dive into the kubernetes architecture.
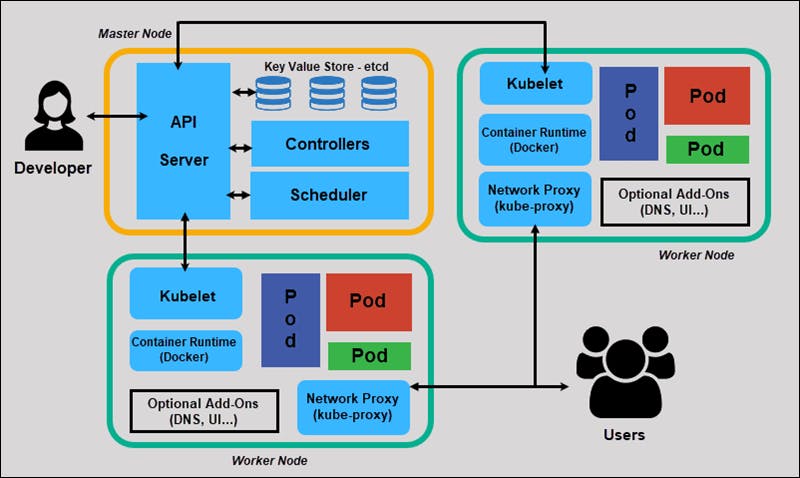
Kubernetes architecture 🏗️
Kubernetes architecture mainly revolves in between the control plane and the nodes in the cluster.
The control plane includes the K8 API server, scheduler, control manager, etcd.
Kubernetes node components include a container run time engine (or) docker, kubelet,kubelet proxy.
Lets get deep dive into each of it
1) API server : It is just like a cluster gateway which gets initial updates of the cluster and queries.
-> It authenticates and authorizes the requests.
->Before creating any new pod or service we have to talk to the API server which validates the requests whether to create a pod or not.
2)Scheduler : The name itself suggests the meaning to it. Scheduler has the whole intelligent way of deciding on which worker node the next pod should be scheduled.
-> It also keeps an eye on how much CPU or RAM space the pod is occupying in the system.
3) Control Manager : It is a daemon which runs the kubernetes cluster using several controller functions.
-> It detects the cluster changes like whenever the pod dies the controller manager detects it and recovers it as soon as possible.
4) etcd : It is just like the cluster brain 🧠 Any changes in the cluster get stored on the key value store.
-> It is also used to store some other config details like ConfigMaps, secrets ,subnets.
-> The main thing is that application data is not gets stored in the etcd.
Now coming on to the Nodes
On every node the 3 processes must be installed for surely they are kubelet, kubeproxy, container run-time.
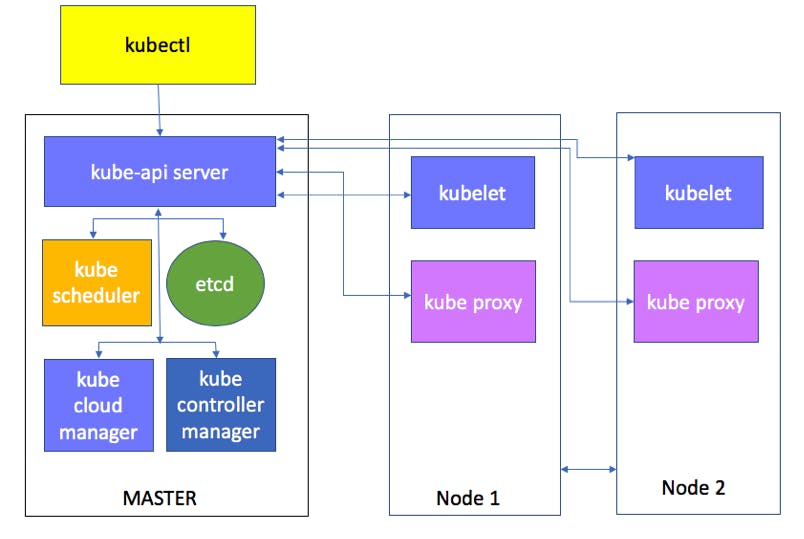
1) Kubelet: It interacts with both the container and the node and it is reponsible for starting and running the pod.
-> The kubelet receives the pod specifications through the API server and executes the action. It also assures the containers are healthy and running.
2) Kube-proxy: It facilitates the kubernetes networking services and it makes sure that services are available for external end points.
3) Container Runtime: Every node runs and manages the container life cycles using a container run time.Kubernetes open container supports Docker, rktnetes.
Pic sources: Google, Learn k8s
Connect with me on:
Protip 💡
At the Begining kubernetes looks overwhelmed to you with many components and objects, but this topic interests me a lot and being consistent in learning is the best way to master it ✅.
