What is CORS in Azure?
I was recently working on a project involving blob storage in Azure. There was something keeping me from uploading my file and it took me forever to figure out what blocked it. It was the freaking CORS settings in Azure. So like a good developer, I went out into the documentation to figure out how to fix it.
After I got my project blob storage working, I realized that even though I had fixed the problem I still didn't know what CORS really was. Now that I kind of know what it is and what it's used for, I'm going to try to briefly explain it to you.
CORS (cross-origin resource sharing) lets you use APIs and data from different origins. An example of this would be using the Google Maps API. You can access that data because they allow your web domain to use it. It also means you'll be able to upload a picture, document, or other data to a blob storage without needing to touch the database first which can be really nice.
Here's a little background about why CORS is even needed. Most web browsers, like Chrome and Firefox, use a security restriction known as same-origin policy. This blocks a web page from calling APIs in a different domain. The reason we don't want to allow calls from different domains is because of the possibility of cross-site scripting attacks. That could take down your website and compromise your database.
That's why it's important to know about CORS. Let's look at an example. Say you are calling an API from google.com on your website corsexample.com. The browser will send your request with an origin HTTP request header. Based on the CORS settings for google.com, you might be allowed through.
If they have their Access-Control-Allow-Origin CORS setting configured to give your domain access, then you're good to go. If they don't have that setting configured to give you access, then you'll get an HTTP error like a 403 server error.
Here's a simple picture of what happens when you aren't an allowed origin.
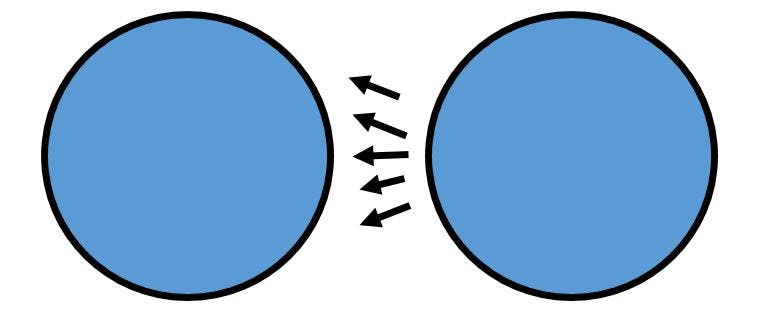
Here's one when you are an allowed origin:
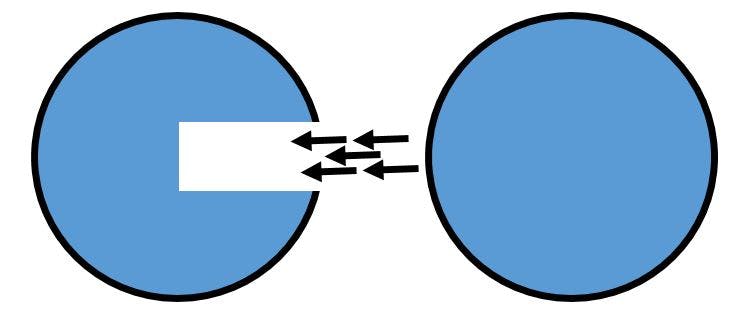
In practice, it's pretty straightforward to use. All you have to do is update a few lines inside of Azure and you're good to go. You can see more about that in their wonderful documentation: [1] [2]
That's what CORS is. It's a defense against scripting attacks that you can make exceptions to. Hopefully this will help you on some of your future projects. At the very least hopefully you could sum up CORS to someone else. Like in an interview…
If you've been trying to make your own little web app but you're still having trouble connecting the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, you aren't alone. Some of my students had that same problem. But on the 18th I'll be doing a webinar to show you how to make a simple web app. It won't take over an hour. You should go sign up if you're interested. https://bit.ly/2DaEZ0F
