"There are 8 ways to do the same thing"
"Should I use inline or block?"
We all have those questions popping in our heads when we try to build something new with HTML / CSS, how the elements are going to be displayed? on top of each other? side by side?
It can be frustrating when you're just starting to learn HTML / CSS.
So, let's take a look at what display property is?
displayproperty tells the browser how elements are going to be rendered by the browser.
There are plenty of display values, we're going to focus on just 4 of them. Those are:
display: block;display: inline;display: inline-block;display: none;
display: block;
- Block-level elements start at a new line and the elements that come after it has to start at a new line.
- It takes up the largest available space.
- We can control width and height of the element.
- Elements are affected by margin and padding.
- Block-level elements stacks on top of each other (like hamburger ingredients).
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Hamburger</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="bun">Bun</div>
<div class="cucumber">Cucumber</div>
<div class="onion">Onion</div>
<div class="bacon">Bacon</div>
<div class="cheese">Cheese</div>
<div class="meat">Meat</div>
<div class="tomato">Tomato</div>
<div class="lettuce">Lettuce</div>
<div class="bun">Bun</div>
</body>
</html>
- As we can see, block-level elements create a new line for preceding and subsequent elements ( div is a block-level element )

display: inline;
- Inline elements take minimum available content space
- We can't control the width and height of the element,
- Only horizontal dimensions are affected by margin and padding properties, element's width and height will remain unaffected.
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Train</title>
</head>
<body>
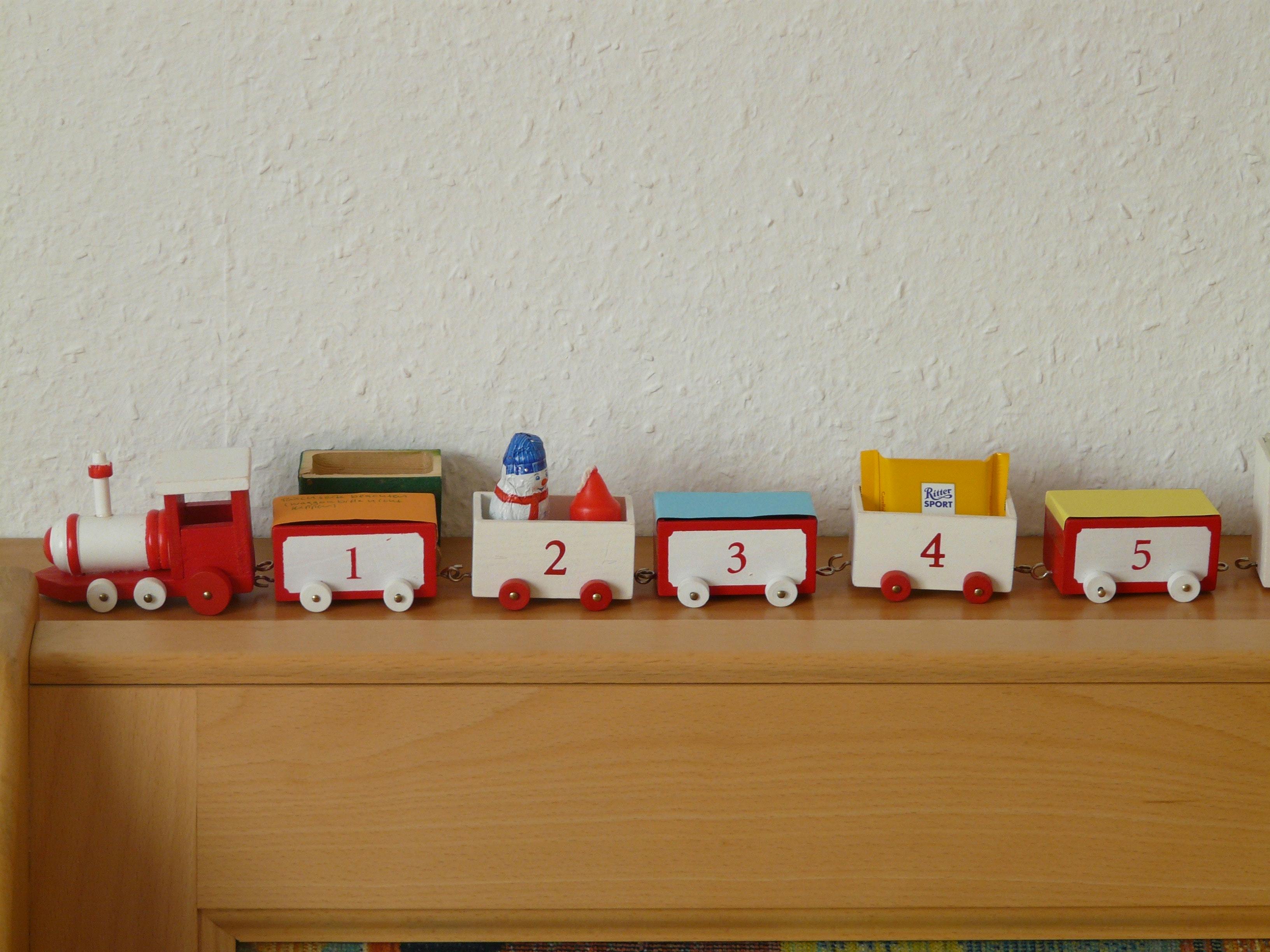
<span class="locomotive">Locomotive</span>
<span class="wagon-1">Wagon 1</span>
<span class="wagon-2">Wagon 2</span>
<span class="wagon-3">Wagon 3</span>
<span class="wagon-4">Wagon 4</span>
<span class="wagon-5">Wagon 5</span>
</body>
</html>
- Inline elements are like train wagons. They stand side by side.

display: inline-block;
- Combination of block and inline elements
- Main difference from inline elements is we can control the width and height properties.
- Elements are affected by margin and padding properties ( both vertically and horizontally ).
display: none;
- It simply hides the element.
- Element that has
display: none;property is not going show up on the screen and other elements will act like it doesn't exist.
Let's take a look at how they interact with each other
We learned what inline, inline-block, block level elements are. It's time to see how they work together.
Imagine you purchased two paintings, a TV, and a TV unit to decorate your favorite corner of the house.
First, you put the TV between the paintings vertically and the TV unit at the bottom. (display: block; on each element)
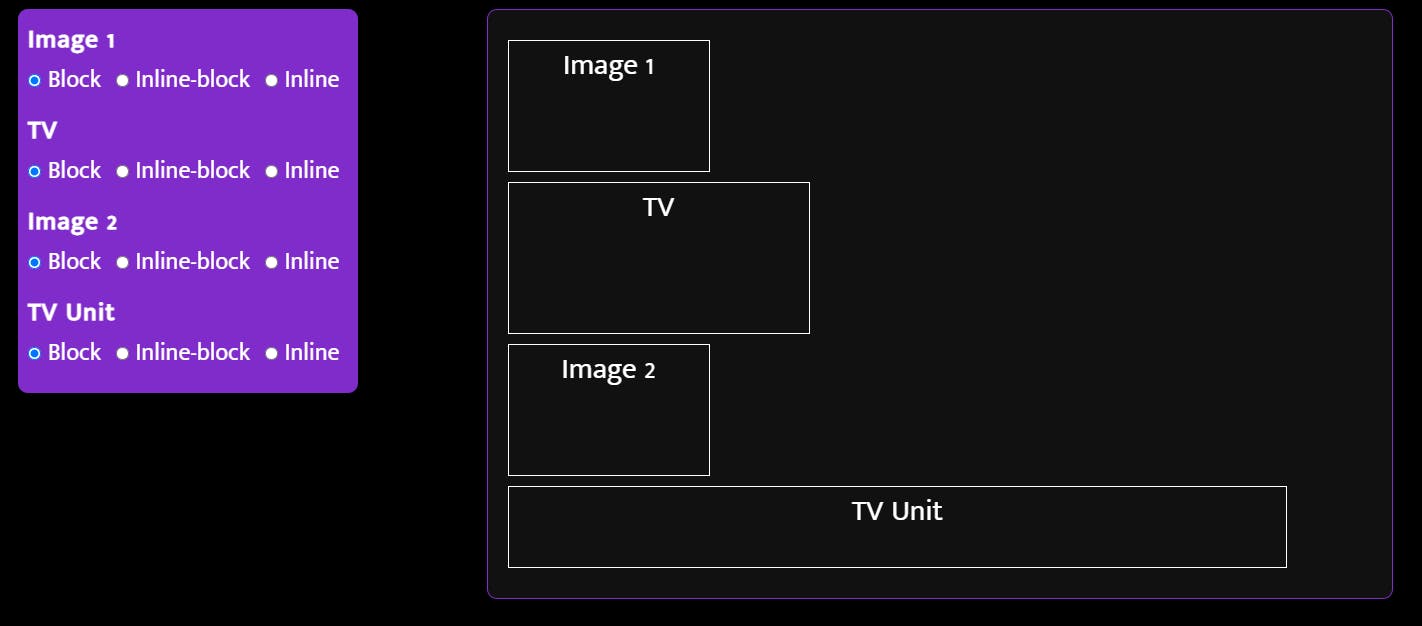
Hmmm, that looks 'fine' but I think we can do better. Let's put paintings and the TV side by side (display: inline;)
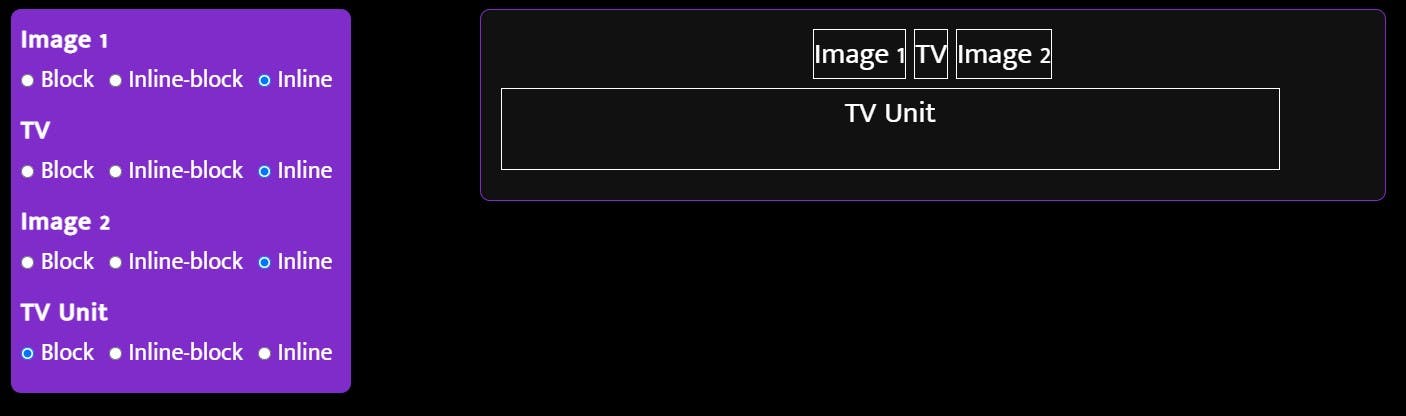
That didn't work either. ( Remember, we cannot control width and height properties of inline elements ) I think we can make it work by giving each of them the space they need. ( display: inline-block; )

Yay, it worked. As a finishing touch, let's center that TV unit at the bottom ( display inline-block at TV unit element ).

So, you might ask how that TV unit is centered automatically. Because we gave text-align: center; property to their parent element.
You can take a further look at this codepen.
That's it folks
If you found this article helpful you can connect me on Twitter for upcoming content, or just come say hi, we can share what we know and learn from each other.