Blockchain and Smart Contracts
The article is a part of a series of articles around blockchain, web3, smart contracts-based projects, and terminologies around it.
Imagine a world where we can send money to our friends or family wherever they are in the world without any centralised banks. A world where we can vote via our smartphone or where we don’t need to wait for authorities approvals to get loans or to get our insurance claim back. A world where we trust the data as it is and counterfeit is not possible. With the series of articles, we will go through what blockchain is, it's underlying technologies, ecosystem and how it revolutionises our world.
Blockchain
Blockchain is a way to store and secure digital data. It is an open ledger that several parties can access at once. One of its primary benefits is that the recorded information is hard to change without an agreement from all parties involved.
Blockchain helps in the verification and traceability of multistep transactions needing verification and traceability. It can provide secure transactions, reduce compliance costs, and speed up data transfer processing.
The data is recorded in chronological order. Also, once the data is recorded, it cannot be changed.
Several industries like Unilever, Walmart, Visa, Tech Mahindra, etc. leverage blockchain technology for greater transparency, security, and traceability. Considering the benefits blockchain offers, it will revolutionise and redefine many sectors. Here are a few case studies which helped us to kick start our Research and Development around Blockchain.
- Walmart uses blockchain to bring unprecedented transparency across their food supply chain network.
- Tech Mahindra's Digital Transformation of Abu Dhabi's Land Registry
- Trade and Finance
- India Explores Blockchain-Based E-Voting By 2024 General Elections
In the series of articles, we will be covering everything around blockchain, smart contracts, web3 and will be working on implementation of following case studies.
- Supply chain management.
- E-Voting.
- Know Your Customer(KYC) chain.
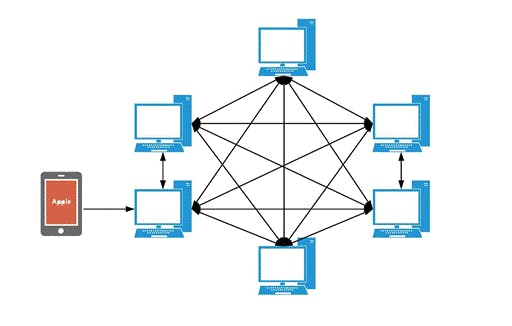
In simple words blockchain is a digital list of data records, which are stored on a distributed database that is shared among the nodes of a computer network. These records compromised of many blocks of data, which are organised in chronological order and are secured by cryptographic proofs.
Since these records are stored on distributed network, hence it guarantees the fidelity and security of a record of data and generates trust without the need for a trusted third party.
History
The first practical implementation of a blockchain is dated back to the early 1990s when computer scientist Stuart Haber and physicist W. Scott Stornetta applied cryptographic techniques in a chain of blocks as a way to secure digital documents from data tampering. Their work inspired many other computer scientist and cryptographic enthusiast, which eventually lead to the creation of first decentralised crypto currency Bitcoin. The Bitcoin white-paper was published in 2008 under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
Similar to Bitcoin, blockchain is a core underlying component of most cryptocurrency networks, acting as a decentralised, distributed and public digital ledger that is responsible for keeping a permanent record (chain of blocks) of all confirmed transactions.
How Blockchain works?
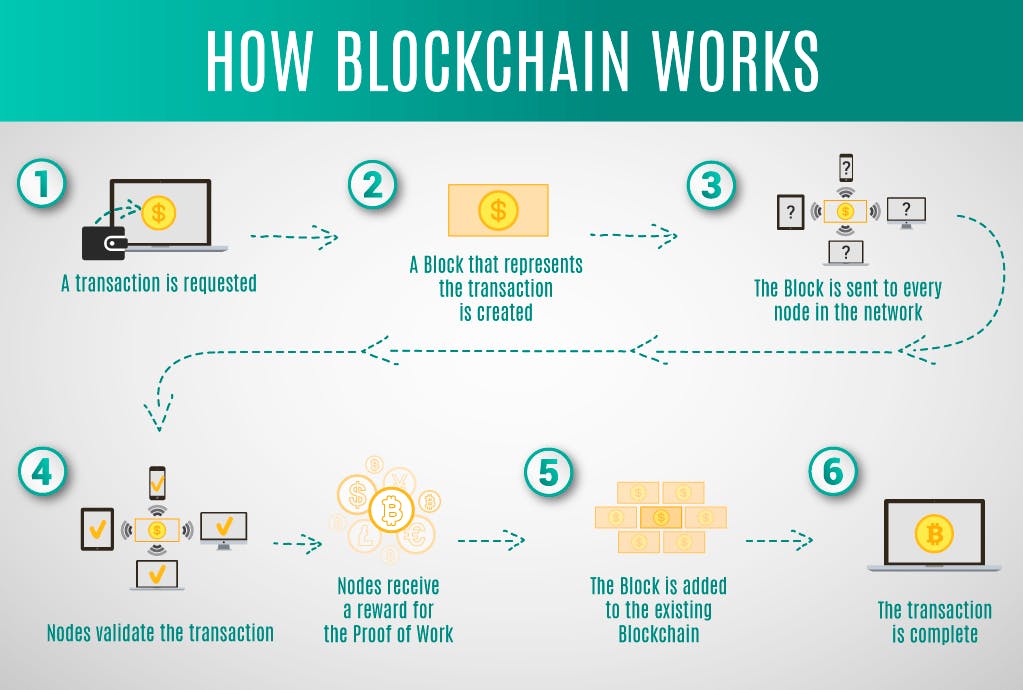
As a distributed ledger technology, blockchain allows information to be distributed but not edited. It is the foundation for immutable ledgers, or records of transactions that cannot be altered, deleted, or destroyed.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are simple piece of code stored on a blockchain that runs when predetermined conditions are met. Smart contracts are basically algorithms that can be proven, managed, and regulated by people all over the world. Hence, anyone can go to the blockchain and regulate it.
How smart contract works?
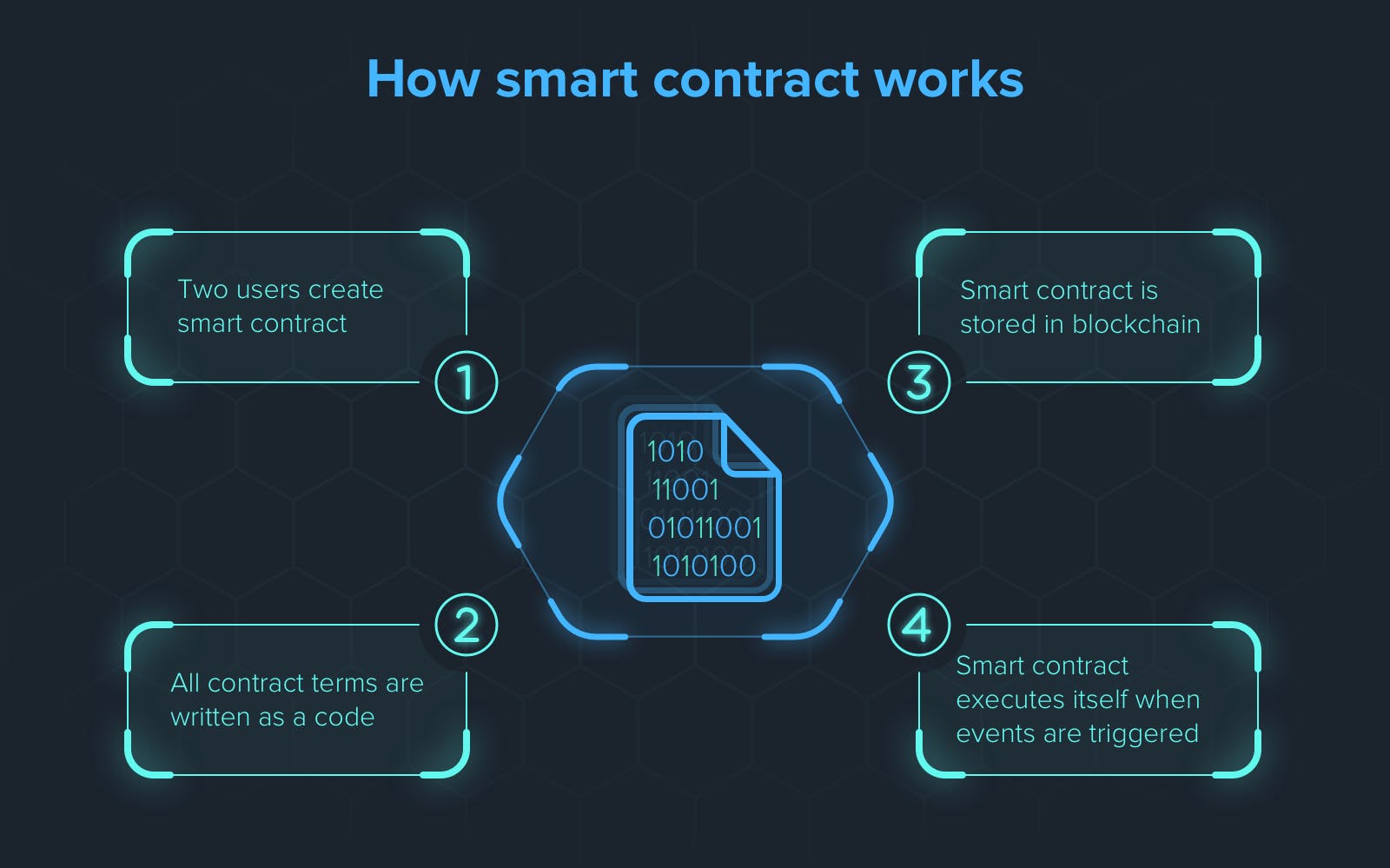
Smart Contracts work by following simple if, else, then... statements that are written into a code in a blockchain. A network of computers also known as nodes executes these statements when predetermined conditions are met and verified. These statements could include actions such as transferring a fund, sending messages or notifications, registering users and so on.
Once these statements are executed, blockchain is updated , which means that transactions cannot be changed and only parties which have been granted relevant permissions can see the result.
How smart contracts are different from traditional contracts?
Smart contracts are computer programs that automate the enforcement of terms where as traditional Contracts are sets of agreed-upon terms which are enforceable by law and are described in a natural, human language.

Benefits of smart contracts
Speed and accuracy - Since smart contracts are digital and automated, there’s no paperwork to process and no time spent reconciling errors that often result from manually filling in documents.
Trust and transparency - Encrypted records of transactions on the network are shared across participants, hence no information can be altered for personal benefit.
Security - Since the transaction records are encrypted, hence each record is connected to the previous and subsequent records on a distributed ledger, as a result in order to change a single record the entire chain of transaction have to be altered.
No Intermediaries - Smart contracts remove the need for intermediaries to handle transactions, since it's regulated by none.

Practical applications of smart contracts.
There are several real-world examples of smart contracts use case, some of them is listed as follows:
Supply chain transparency - Companies across the globe are using smart contracts to quickly resolve disputes with vendors and suppliers. Through real-time communication and increased visibility into the supply chain, they are building stronger relationships with suppliers, resulting in more time for critical work and innovation. Especially in pharmaceuticals industries.
International Trade and finance - International money transfers usually come in the form of Paypal or wire transfers. These transactions include hefty fees of $15 to $45 per transaction. With smart contracts, the blockchain knows no borders. As long as the recipient and sender can access the same blockchain that the transaction is using then the transaction can be made with only the fees associated with the blockchain.
Voting - Allegations of voting fraud occurs even across stable democracies such as USA and India. Smart contracts can be used to validate a voter‘s identity and record their vote. Since the blocks within a blockchain are impossible to alter once they have been recorded, manipulation of this record would not be possible.
Property Ownership - Within the housing market, smart contracts can be used to record the ownership of all types of property from buildings, land to houses.
Challenges facing Smart Contracts
Scalability - One of the major challenges facing smart contracts is the scalability. For example, currently on Ethererum network can handle upto 30 transactions per second. However as per Vitalik Buterin, Ethererum 2.0 will be able to process 100,000 transactions per second.
Execution Risk - Intrinsic errors or bug in the contract can result in unintended behaviour. Anonymous persons can exploit these loopholes and can kill the contract library.
Why Smart Contracts Will Change the World?
The simple reason is blockchain community. People are sick of banks and banking regulations. Oligarchs in collaboration with banks are stealing money from the hands of their citizens. The blockchain community around the world are on a mission to solidify agreements and making sure that agreements 100% go through smart contracts.
Smart contracts maybe not be 100% foolproof but they are close, and they are putting more power in the hands of the citizens.
What next?
As we discussed above that blockchain is growing list of records, these records are linked together using cryptography. Cryptography is the heart and soul of blockchain, as it's the underlying mechanism as how blockchain provides secure transactions and communications, safeguard personal identifiable information and other confidential data. In the next article we will look at cryptography and various type of cryptography used in blockchain.
This article is part of Research & Development work being done by Pushkar Kumar Suresh konakanchi and Ruchika Gupta.. We will be covering a series of articles along with open source projects around blockchain, smart contracts, and web3 in general. Here is the list of all the articles that you can follow to start with Blockchain and write your first contract.