Simplify your JavaScript with these array methods!!
======================================================
Array Methods 😬
1. ITERATION METHODS :
- Examination Methods : Observe the context of an Array.
- Transformation Methods : Derive a new array from receiver.
- Reduction Methods : Compute a result based on the receiver’s element.
- From Loops : Iterating Arrays from Loops.
1.1 Examination Methods
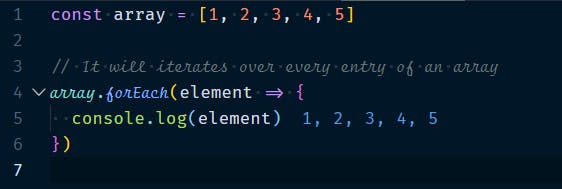
1.1.1 Array.forEach(callback, thisValue?)
Iterates over the every entry of an array. It takes a callback function where you can code. You cannot break out of it or return a value from it.
Example :
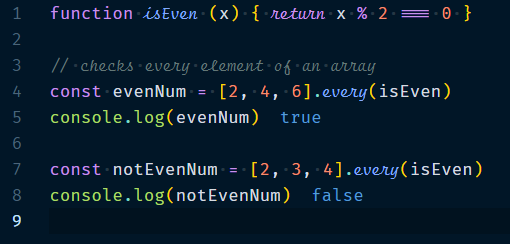
1.1.2 Array.every(callback, thisValue?)
Returns true, if the callback returns true for every element. It will stop iteration as soon as the callback return false.
Example :
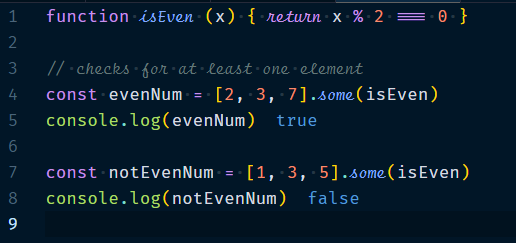
1.1.3 Array.some(callback, thisValue?)
Returns true, if the callback returns true for at least one element. It stops iteration as soon as the callback returns true.
Example :
1.2. Transformation Methods
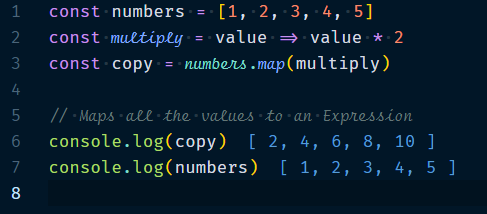
1.2.1 Array.map(callback, thisValue?) : Copy while giving new values to elements.
This will map all the values to an expression & returns a modified copy of the array leaving original untouched.
Example :
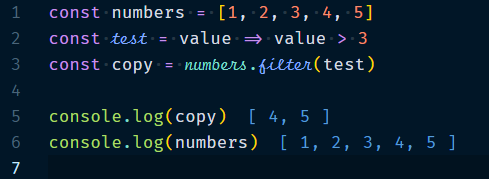
1.2.2 Array.filter(callback, thisValue?) : Only keep some of the elements.
This will only keep the elements which will match the condition & returns modified copy of the array leaving original untouched.
Example :
1.3. Reduction Methods
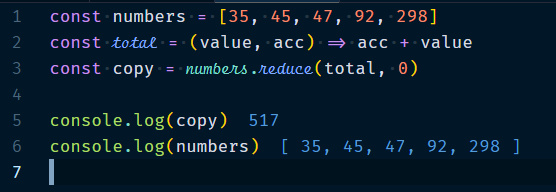
1.3.1 Array.reduce(callback, initialValue?) : deriving a value from an Array
This will reduce all the elements to a single value & reducer function total takes value and accumulator. Accumulator is required to be set to a starting value & returns modified copy of the array leaving original untouched.
Example :
1.4. Iterating Arrays from Loops
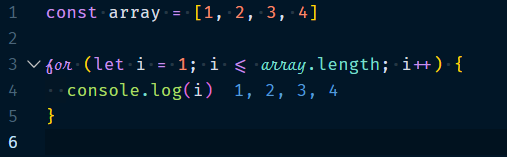
1.4.1 For Loops
The for loop is one of the basic loops for looping through an array. It takes a starting index and then loops through to the ending index.
Index === Integer.
Example :
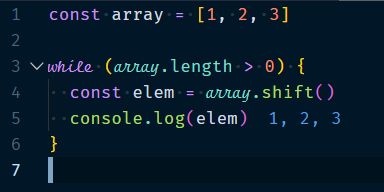
1.4.2 While Loops
The while loop will loop whenever a condition stays true. This code below uses a while loop. In each loop iteration, it removes the first element of array via shift() and logs it.
Example :
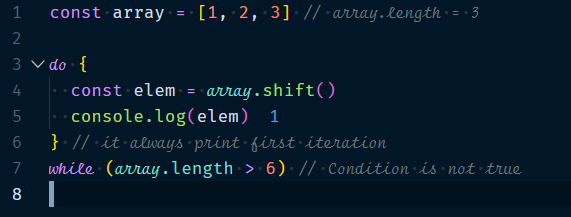
1.4.3 Do-while Loops
The do-while loop works much like while loops, but it will check its condition after each loop iteration(not before) & it will always execute first iteration.
Example :
2. ARRAY CONSTRUCTOR METHODS :
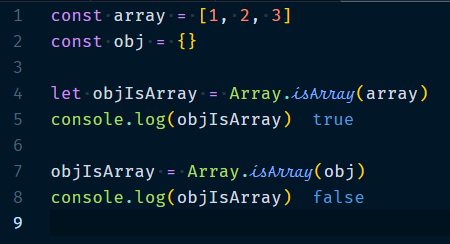
2.1 Array.isArray(object)
Returns true if object is an array. It is a convenient way to check if the element is an array.
Example :
3. ARRAY PROTOTYPE METHODS :
These are grouped by functionality :
- Destructive : They change the arrays that they are invoked on.
- Non-Destructive : They don’t modify their receivers, such methods often return new arrays
3.1. Destructive Methods
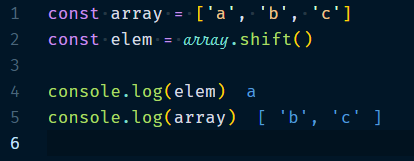
3.1.1 Array.shift()
Removes the element at index 0 and returns it. The indices of subsequent elements are decremented by 1.
Example :
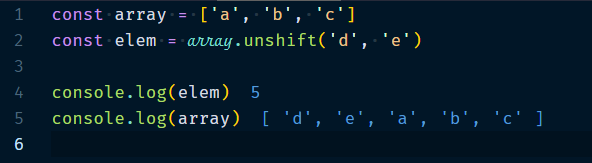
3.1.2 Array.unshift(elem1?, elem2?, …)
Prepends the given elements to the array. It returns the new length.
Example :
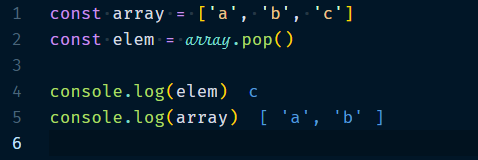
3.1.3 Array.pop()
Removes the last element of the array and returns it.
Example :
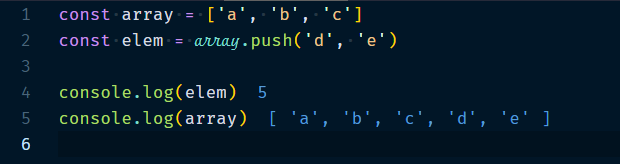
3.1.4 Array.push(elem1?, elem2?, …)
Adds the given elements to the end of the array. It returns the new length.
Example :
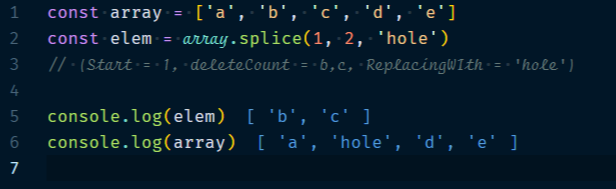
3.1.5 Array.splice(startIndex, delete Count?, elem1?, elem2?, …)
Starting at startIndex, removes delete-Count elements and insert the given elements. In simple words, we are replacing the delete-count elements at position startIndex with elem1, elem2, and so on. This method returns the elements that have been removed.
Start can be negative = (-1) refers the last element, and so on.
Example :
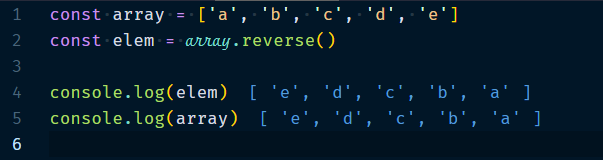
3.1.6 Array.reverse()
Reverse the order of the elements in the array and returns a reference to the original(modified) array.
Example :
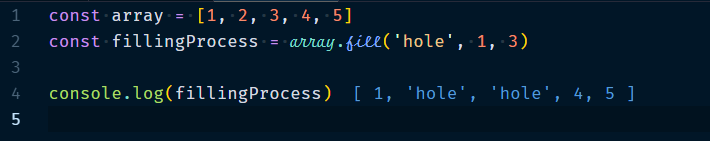
3.1.7 Array.fill(new-element, start-index, end-Index)
Array.fill will add or replace the element with the element specified from start Index to end Index. If start Index is not defined then it will start from 0, if end index is not defined, then it will change values up to end of the array.
Example :
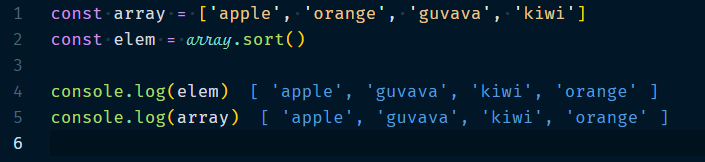
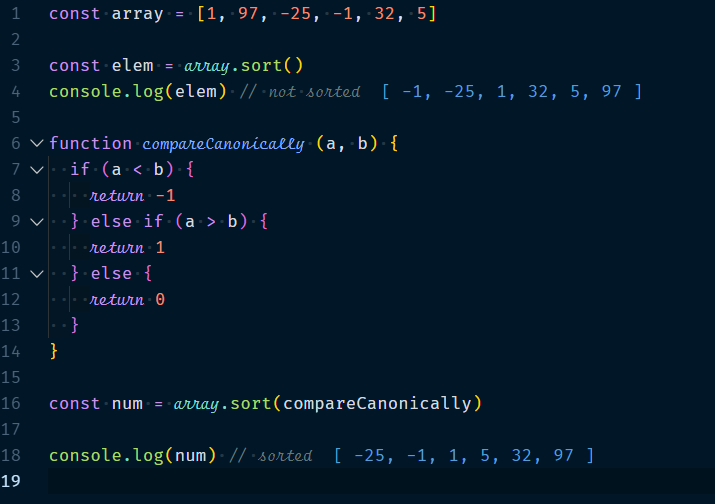
3.1.8 Array.sort(compare-function?)
It will sort the array and returns it. This sorting compares values by converting them to strings, which means that numbers are not sorted numerically we can fix this by providing the optional parameter compareFunction().
Example :
3.2 Non-Destructive Methods
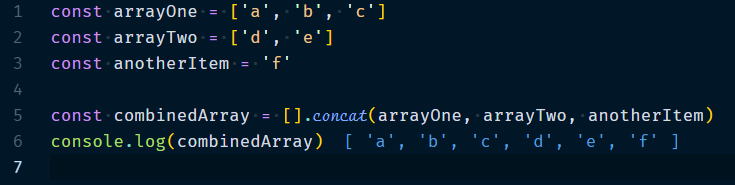
3.2.1 Array.concat(arr1?, arr2?, … )
Creates a new array that contains all the elements of the receiver, if one of the parameters is not an array, then it is added to the result as an element. so if we can say in simple words, it will add different array elements to the new array.
Example :
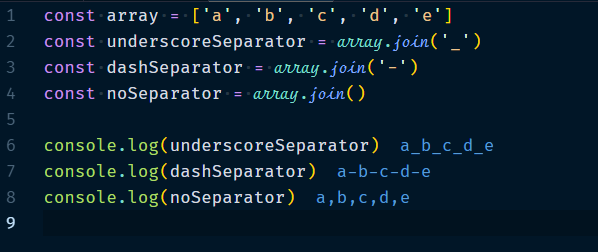
3.2.2 Array.join(separator?)
This will return a string by concatenating the entries after they are converted to string with the separator between each entry. Works best with the string and number arrays. If separator is omitted, ',' is used.
Example :
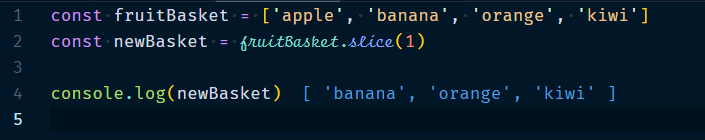
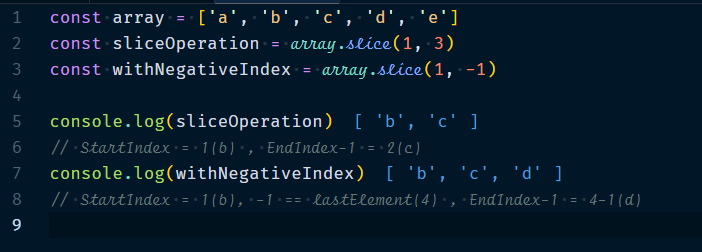
3.2.3 Array.slice(startIndex?, endIndex?)
It will copy array elements into a new array, starting at start Index, until and excluding the element at end Index,which means start Index to endIndex-1. If either of the indices is negative then the array length is added to it, thus, (-1) refers to the last element, and so on.
Example :
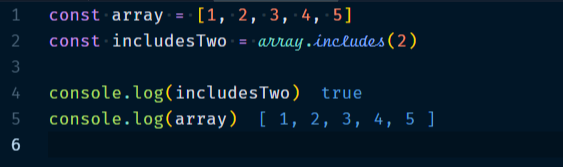
3.2.4 Array.includes()
Array.includes() checks if an item exits in an array. It takes a number or string which the function can compare.
Example :
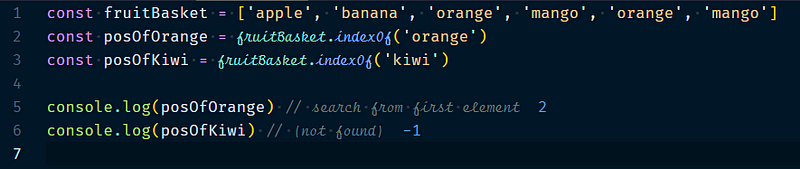
3.2.5 Array.indexOf(searchaValue, startIndex?)
It will search the array for search Value, starting at start Index. It returns the index of the first occurrence or if nothing is found it returns -1. if start Index is negative, the array length is added to it & if it is missing, the whole array is searched.
Example :
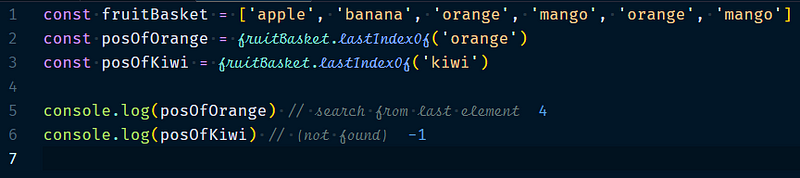
3.2.6 Array.lastIndexOf(searchElement, startIndex?)
It will search the array for search Element, starting at start Index, backward. It returns the index of the first occurrence or if nothing found it returns -1.
Example :
4. SOME OTHER IMPORTANT ARRAY METHODS :
4.1 Remove Duplicates in Array
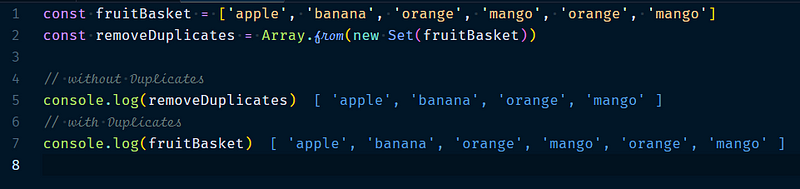
4.1.1 Array.from(new Set(array))
Set is an object that cannot have duplicates entries. You can create a new Set from an array then convert it back to an array.
Example :
4.2 Find Element in Array
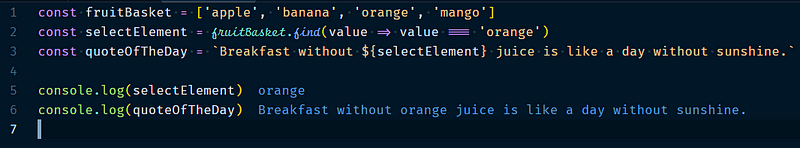
4.2.1 Array.find()
Array.find will return the element in the array with the given condition. Example, if we want to get certain elements from array & work on that element separately.
Example :
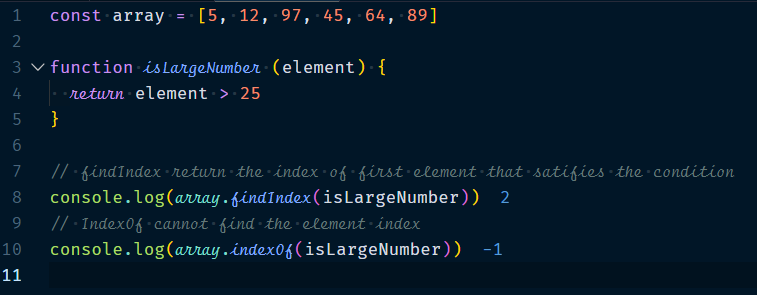
4.2.2 Array.findIndex()
Array.findIndex will return the index of the element in the array with the given condition. it is same as indexOf method but only difference is indexOf only works with primitive values. if you wish to find an object(array, object or function) in the array, you need to use method findIndex.
Example :
======================================================
Manipulation of Arrays with just Array.slice() and Array.concat().
There are so many methods like push, pop, shift, unshift, and splice because they're easier to use as a beginner, if we open any book or website, they have used these methods to manipulate the arrays. But these methods mutate arrays to ensure arrays don't mutate. you can use slice and concat over these five methods As these two are non-destructive methods which doesn't modify the existing array and they will return a new array.
1. Adding Elements
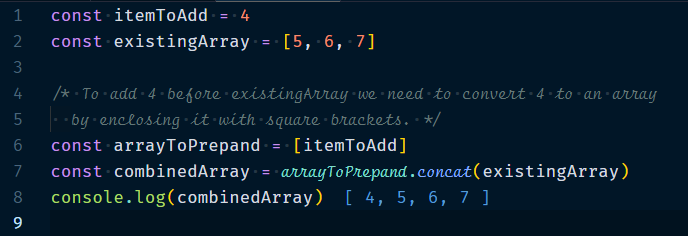
1.1 Adding elements to the beginning of array.
- Convert elements into an array(if they’re not one already)
- Combine the arrays together with
concat
Example :
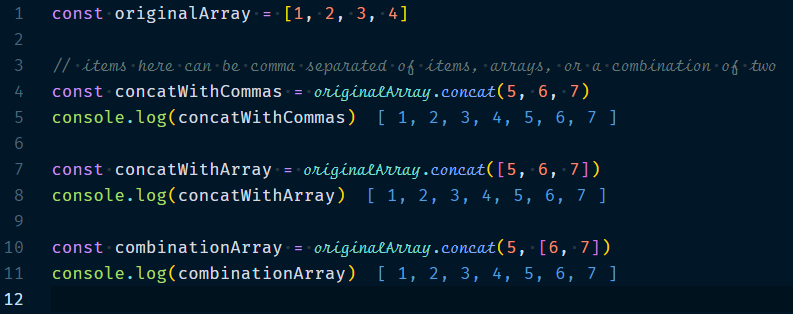
1.2 Adding elements to the end of array
We can add elements to the end of an array with a method called concat.
Example :
1.3 Adding elements to the middle of an array
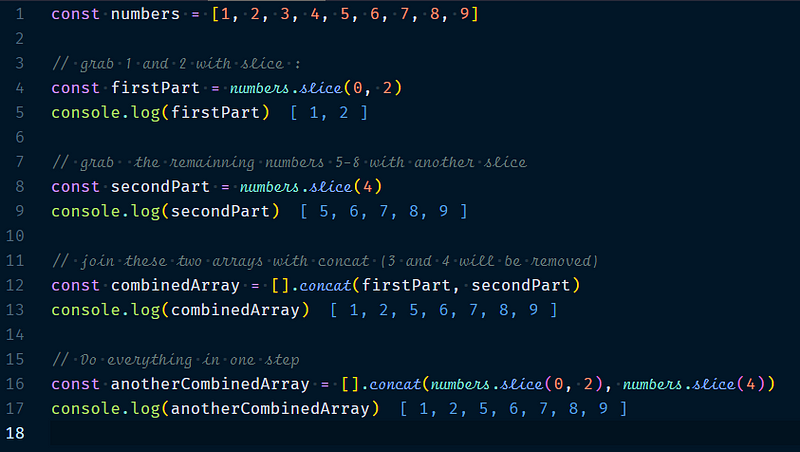
The idea is to add elements to the middle of an array is to split your array into two parts with slice then join three arrays together in this sequence : first part, items to add, second part.
Example :
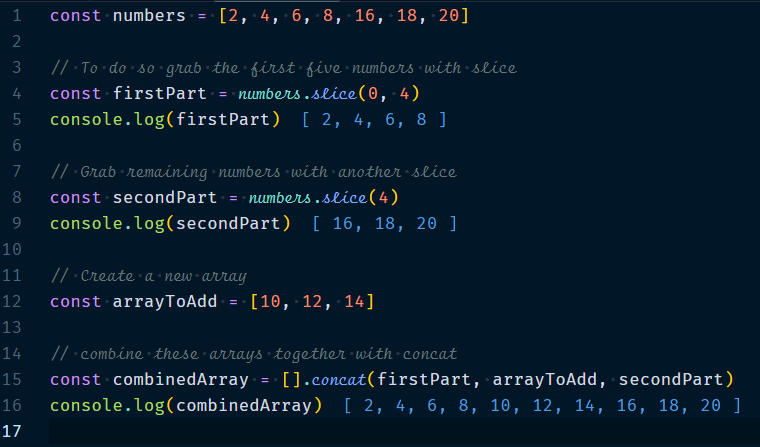
2. Removing Elements
2.1 Removing elements from the front
We can remove elements from the front of an array with a method slice.
Example :
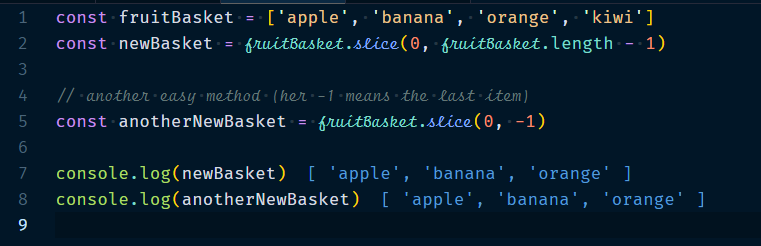
2.2 Removing elements from the end
We can use same method to remove elements from the front of an array. but first we will need to pass correct endIndex value. So that you can remove the last item and can use Array.length - 1 as your endIndex value.
Example :
2.3 Removing elements from the middle
Removing elements from the middle of an array is trickier then to removing item from the end. The idea is to copy the parts you want to retain with slice then join the copied arrays together with concat.
Example :