Wheee! So, today we’re gonna see how actually we can set up routes such as /home ,/about And much more for a ReactJs application. People define ReactJs as a JavaScript framework to develop single-page applications, but that’s a myth as we can add a bunch of other pages on a specific route to render our components on a whole different page🗒️
Need of routing in web-apps ✨
If I want to define Routing, I would define it as a system for resource navigation. Routing usually means matching components (the resource people want) to a URL (the way of telling the system what they want).
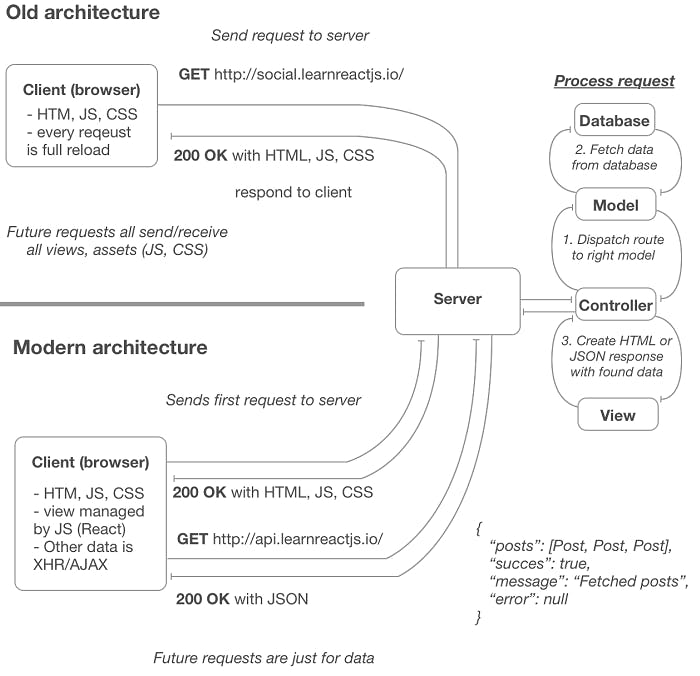
In the old architecture, the server was used to fetch data from the database and then populate it to the specific Html view templates sent to the client. In the modern approach, more application logic on the client is managed by JavaScript (in our case, React). The server initially sends the Html, JavaScript, and CSS assets, but after that, the client React app takes over. From there, unless a user manually refreshes the page, the server sends raw JSON data.
Let’s learn about some of the terminologies while dealing with react-routing. ✨
Three primary categories of components in react-router:
Routers, like
<BrowserRouter>and<HashRouter>Route matchers, like
<Route>and<Switch>And navigation, like
<Link>,<NavLink>, and<Redirect>
All of the components that you use in the web app should be imported from react-router-dom.
Now, let’s dive somewhat more deeply into what these 3 categories of components stand for.
Routers: At the core of every react-app, there should be a router component. For web projects, react-router-dom it provides <BrowserRouter>. A <BrowserRouter> uses regular URL paths. Specifically, your web server needs to serve the same page at all URLs managed client-side by React Router.
Route matches: There are two route matching components: Switch and Route. When a <Switch> is rendered, it searches through its children <Route> elements to find one that path matches the current URL. When it finds one, it renders that <Route> and ignores all others. This means that you should put <Route>s with more specific (typically longer) paths before less-specific ones.
Take a note of an important thing, the <Route path> matches to the beginning of the URL and not the whole thing. So, that is why we put the shorter paths in the end to get the least possibility of getting matched. Also, the shortest path that <Route path> can expect is <Route path="/">
Navigation or Route changers: This provides a <Link> component to create links in your application. Wherever you render a <Link>, an anchor () will be rendered in your HTML document.
Any time that you want to force navigation, you can render a <Redirect>. When a <Redirect> renders, it will navigate using its to prop.
Let’s see some code part of routing in react ✨
import react from "react";
import {
BrowserRouter as Router, //creating an alias of BrowserRouter
Switch,
Route,
Link
} from "react-router-dom";
export default function App(){
return(
<Router>
<div>
{/*The below part will render an anchor tag in HTML doc*/}
<Link to="/"></Link>
<Link to="/about"></Link>
<Link to="/contact"></Link>
{/*A <Switch> looks through its children <Route>s and
renders the first one that matches the current URL.*/}
<Switch>
<Route path="/about">
<About />
</Route>
<Route path="/contact">
<Contacts />
</Route>
<Route path="/">
<Home />
</Route>
</Switch>
</div>
</Router>
)
};
function Home() {
return <h2>Home</h2>;
}
function About() {
return <h2>About</h2>;
}
function Contacts() {
return <h2>Contacts</h2>;
}
Finally😤, we’re done with adding routes to the React application. So, from the above dummy components, you can surely learn out how you can actually add routing to the so-called SPA (Single Page Application) using ReactJs. And it is much easier than it seems, so go get your React application some routes and thank me later 😎