Here we are with the buzzing topics: Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Mixed Reality (MR) and eXtended Reality (XR). All these form a subset of the huge, towering, revolutionary Metaverse. The three of these realities (with XR being the umbrella term for all) differ in quite a few prospects yet share common over-lapping features. We will briefly discuss their features, the coolest apps in the technology and then summarise the differences in a tabular format.
Augmented Reality (AR)
 AR technology enables us to view digital elements in our real-time environment. It requires the user to hold a smartphone camera in front of them. Most common AR applications include Snapchat Lenses or games like Pokémon Go. The experience provided by AR is not holistic as the computer-generated and real-world content do not interact with each other.
Some of the coolest AR apps include BooksARlive where every page of the book turns into an interactive scene, IKEAPlace to place furniture virtually in your house, and Parker- your very own virtually-real pet.
AR technology enables us to view digital elements in our real-time environment. It requires the user to hold a smartphone camera in front of them. Most common AR applications include Snapchat Lenses or games like Pokémon Go. The experience provided by AR is not holistic as the computer-generated and real-world content do not interact with each other.
Some of the coolest AR apps include BooksARlive where every page of the book turns into an interactive scene, IKEAPlace to place furniture virtually in your house, and Parker- your very own virtually-real pet.
Virtual Reality (VR)
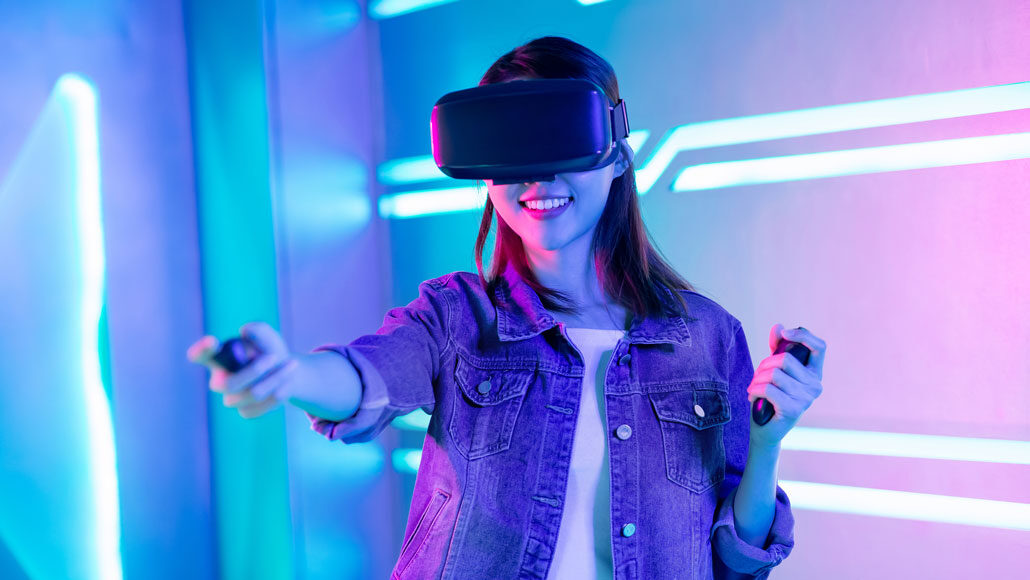 VR completely replaces a user's view by immersing them in a three-dimensional, digitally generated environment. Many people know VR through the use of Head-Mounted Devices (HMD) like the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, or Google Cardboard. It currently has applications in the fields of gaming, education and healthcare. A true VR is said to engage all 5 senses (taste, sight, smell, touch, and sound).
Some of the best VR Apps of 2022 are Space Explorers: The ISS Experience, Within VR (storytelling), and The Guardian VR (news stories).
VR completely replaces a user's view by immersing them in a three-dimensional, digitally generated environment. Many people know VR through the use of Head-Mounted Devices (HMD) like the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, or Google Cardboard. It currently has applications in the fields of gaming, education and healthcare. A true VR is said to engage all 5 senses (taste, sight, smell, touch, and sound).
Some of the best VR Apps of 2022 are Space Explorers: The ISS Experience, Within VR (storytelling), and The Guardian VR (news stories).
Mixed Reality (MR)
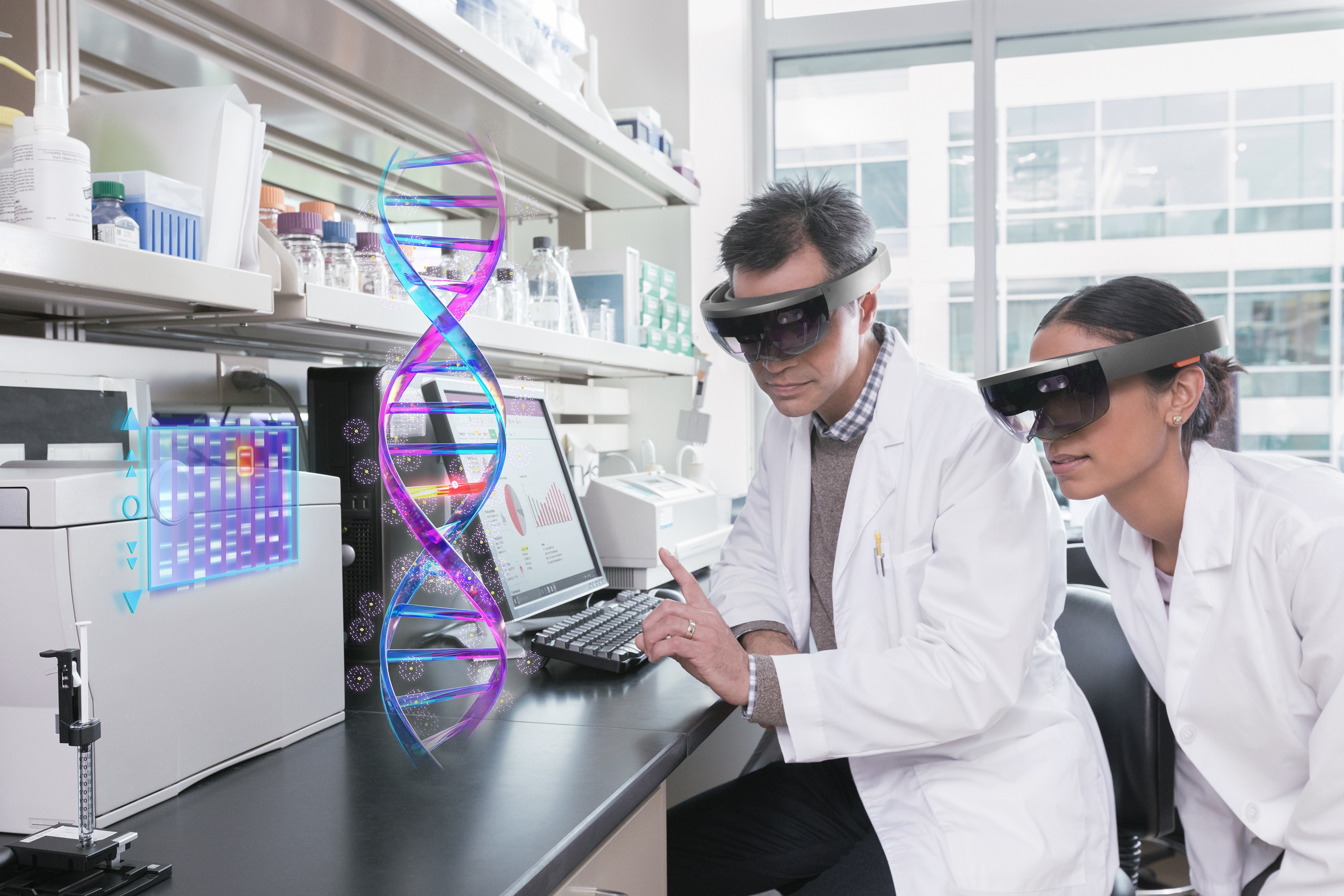 Also referred to as Hybrid Reality, MR removes the boundary between real and virtual interaction. Computer-generated objects can be placed in the real world. The synthetic content and the real-world content can react to each other in real-time. Examples of MR include games like Halo Recruit or apps such as HoloTour.
Microsoft’s HoloLens, a wearable holographic computer, could potentially become commonplace in schools, colleges, hospitals, and find use in a multitude of other professions.
Also referred to as Hybrid Reality, MR removes the boundary between real and virtual interaction. Computer-generated objects can be placed in the real world. The synthetic content and the real-world content can react to each other in real-time. Examples of MR include games like Halo Recruit or apps such as HoloTour.
Microsoft’s HoloLens, a wearable holographic computer, could potentially become commonplace in schools, colleges, hospitals, and find use in a multitude of other professions.
Extended Reality (XR)
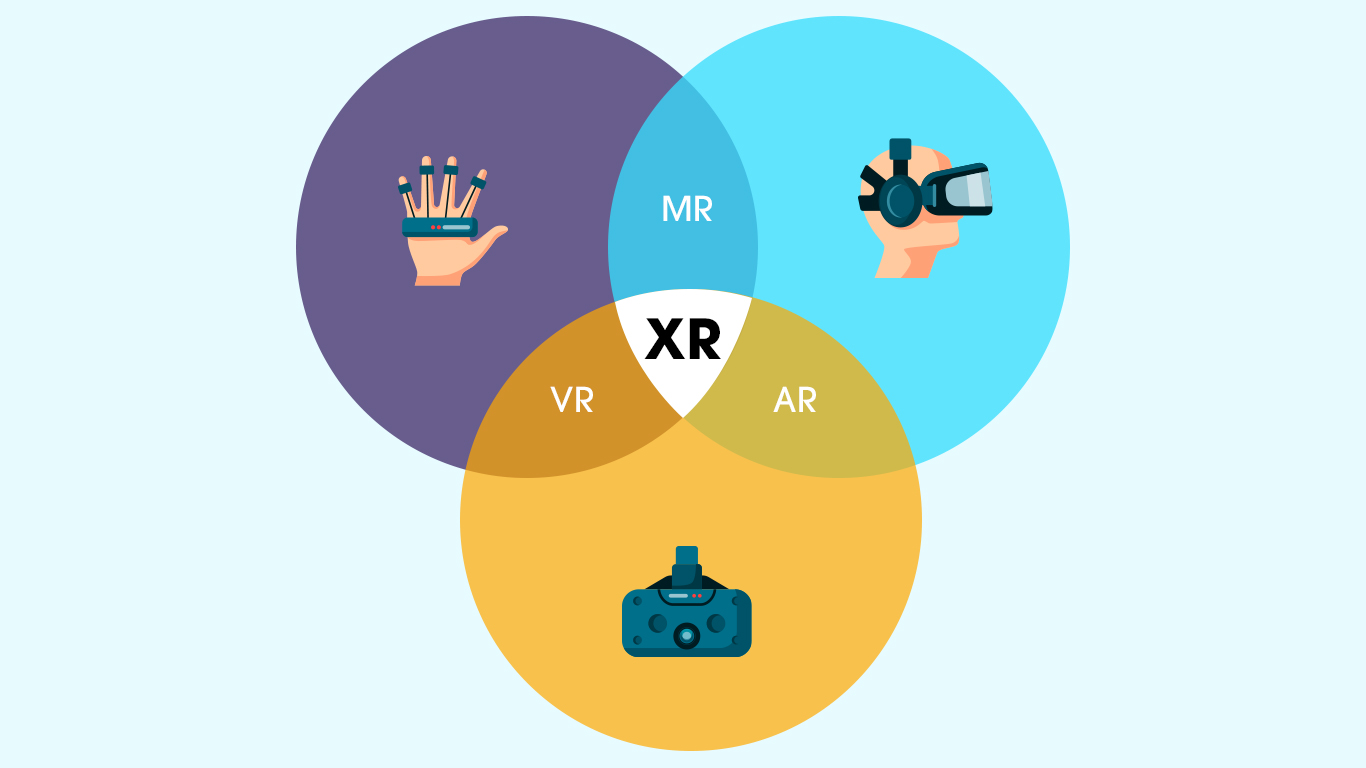 XR is an umbrella term for all three realities viz. AR, VR and MR. It refers to all real-and-virtual combined environments and human-machine interactions generated by computer technology and wearables. The 'X' in XR is simply a variable that can stand for any letter.
XR is an umbrella term for all three realities viz. AR, VR and MR. It refers to all real-and-virtual combined environments and human-machine interactions generated by computer technology and wearables. The 'X' in XR is simply a variable that can stand for any letter.
Here is a comparison between the 3 realities:
| Augmented Reality | Virtual Reality | Mixed Reality | |
| Real/Virtual | Real-world environment overlaid with virtual objects. | Fully virtual environment. | Combination of the real and virtual world. |
| Devices Required | Smartphones | Head Mounted Devices | Head Mounted Devices |
| Interaction | Real and digital content do not interact. | Actions can be performed in the virtual world. | Real and virtual content can interact. |
| Advantages | Brings products to life, Visualisation, Appealing UX. | Realistic scenarios, interesting and engaging. | Expands viewer's worldview, digital information is laid on top of real-world objects. |
| Software used | Unity ARCore, ARKit, Vuforia | Unreal Engine 4 | Google ARCore, Apple ARKit |
| Applications | Google Lens, YouCam, Snapchat. | Google Earth VR, Sinespace. | Microsoft Hololens. |