PostgreSQL is a powerful, open-source object-relational database system. PostgreSQL language, such as create a database, drop a database, select database, select table, update a record, create a table, delete record, drop table, triggers, functions, insert the record, cursors.
Set up PostgreSQL
Download PostgreSQL from here. After installation is done you need to search for Pgadmin.
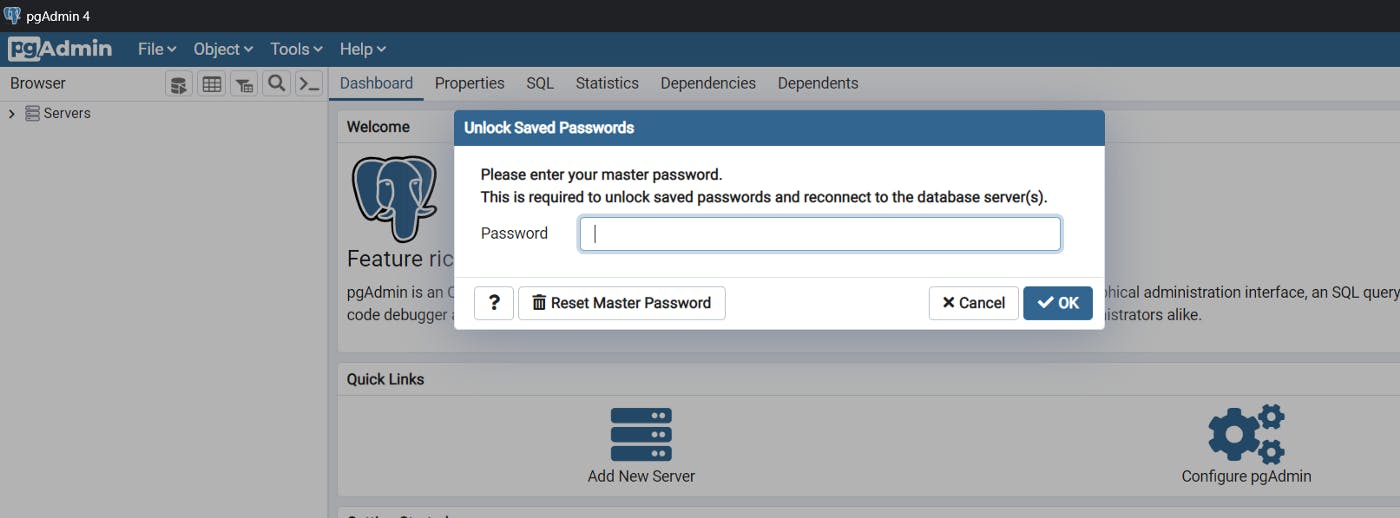
You need to set a master password for security purposes.
Now you are able to see the dashboard for pgAdmin.
Create a Server
Add the Server name which you want to give.
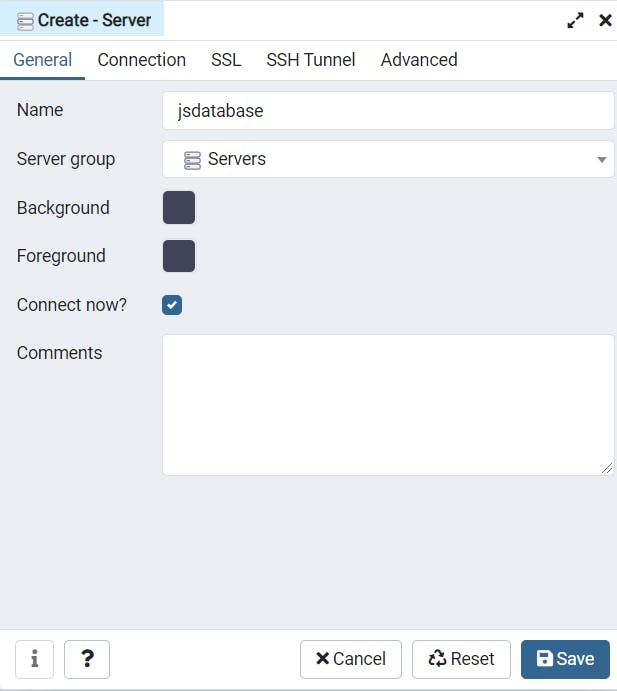
Add hostname and password.
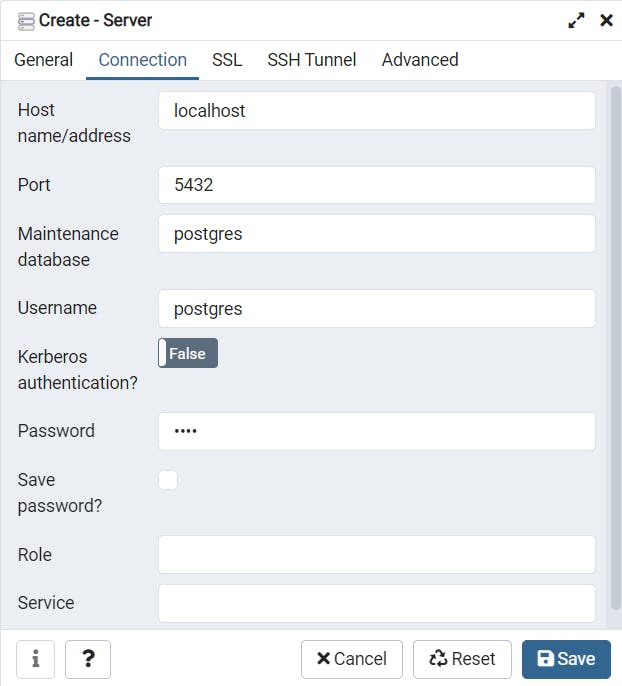
Now you can see the server jsdatabase created successfully
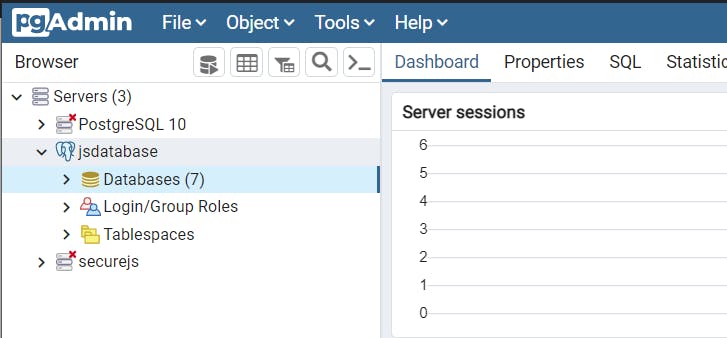
Create Database
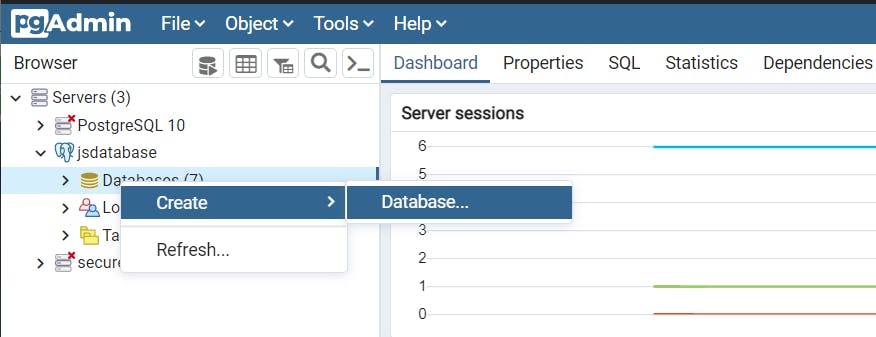
Add database name.
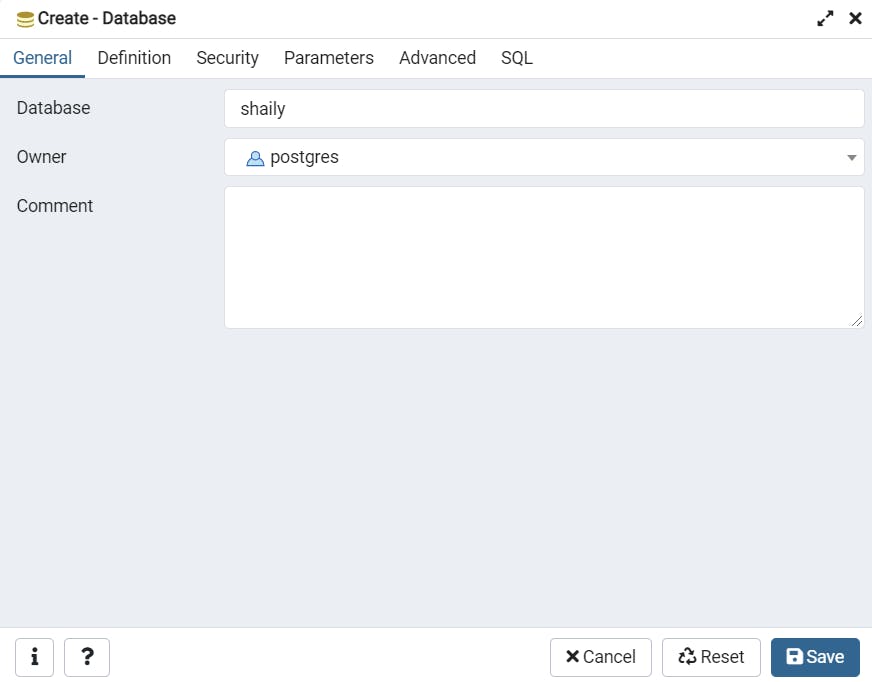
shaily database created successfully.
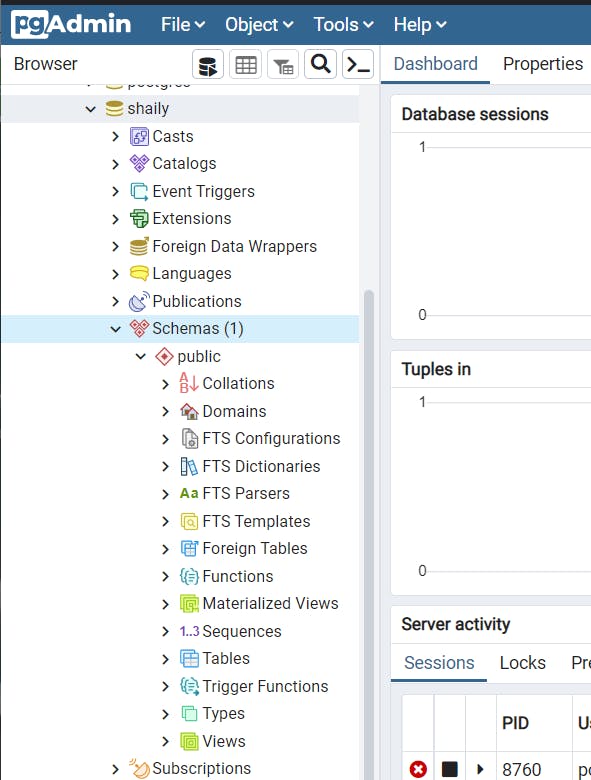
In Schemas you can create a database table.
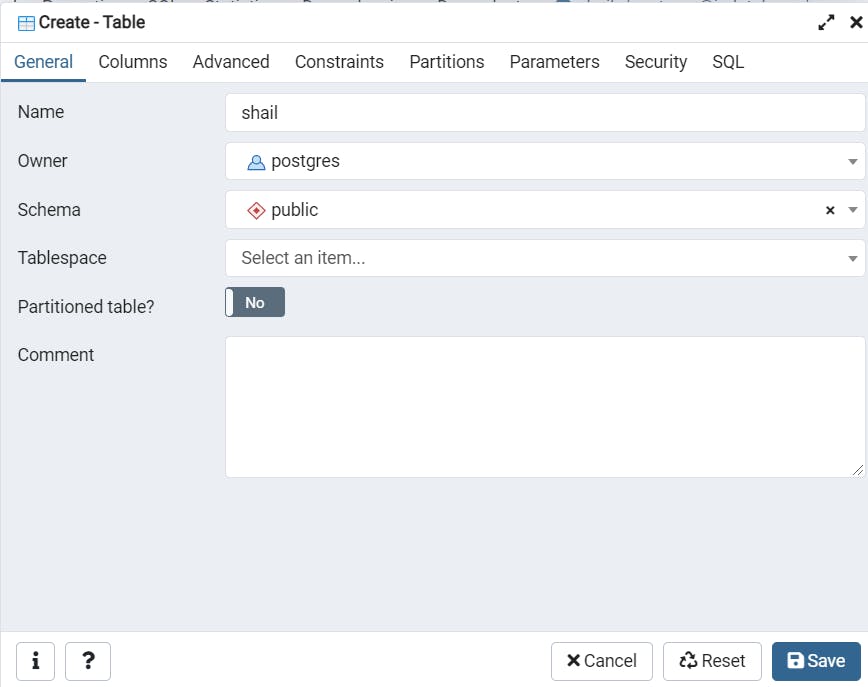
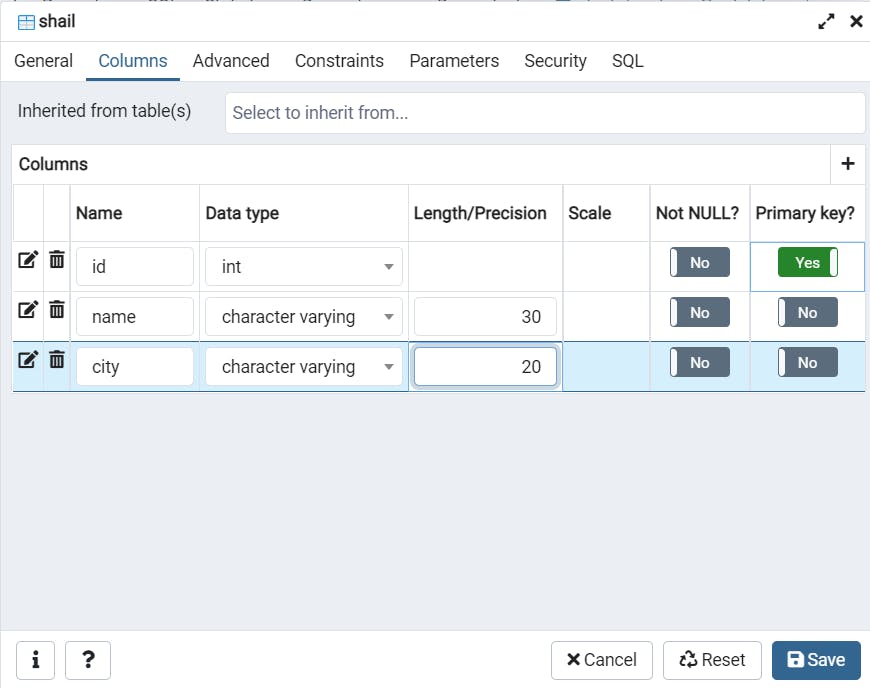
Add columns using datatype.
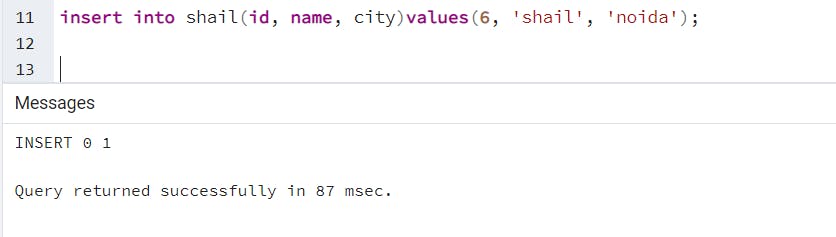
Open query editor, and insert data into a table using the following query.
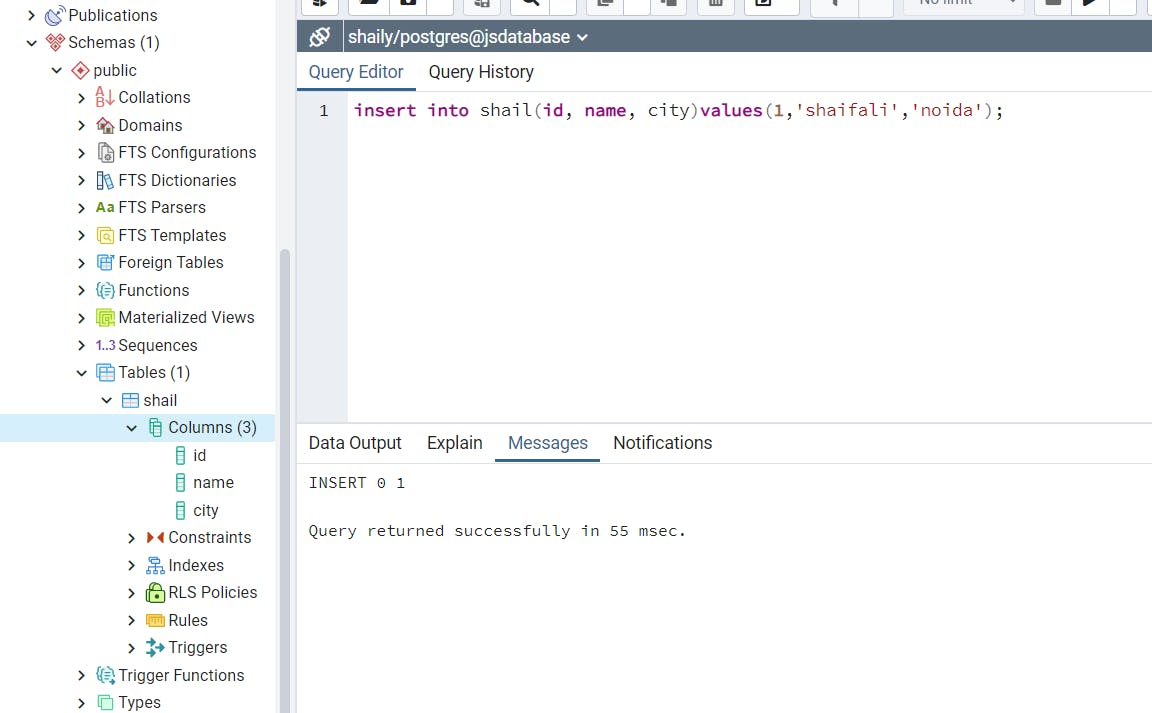
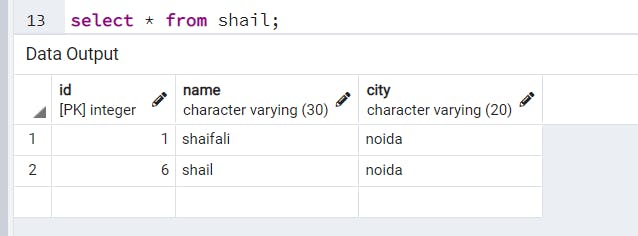
Show table data. Datatypes are supported by PostgreSQL.
- Boolean
- Character Types [ such as char, varchar, and text]
- Numeric Types [ such as integer and floating-point numbers]
- Temporal Types [ such as date, time, timestamp, and interval]
- UUID [ for storing UUID (Universally Unique Identifiers) ]
- Array [ for storing array strings, numbers, etc.]
- JSON [ stores JSON data]
- hstore [ stores key-value pair]
- Special Types [ such as network address and geometric data]
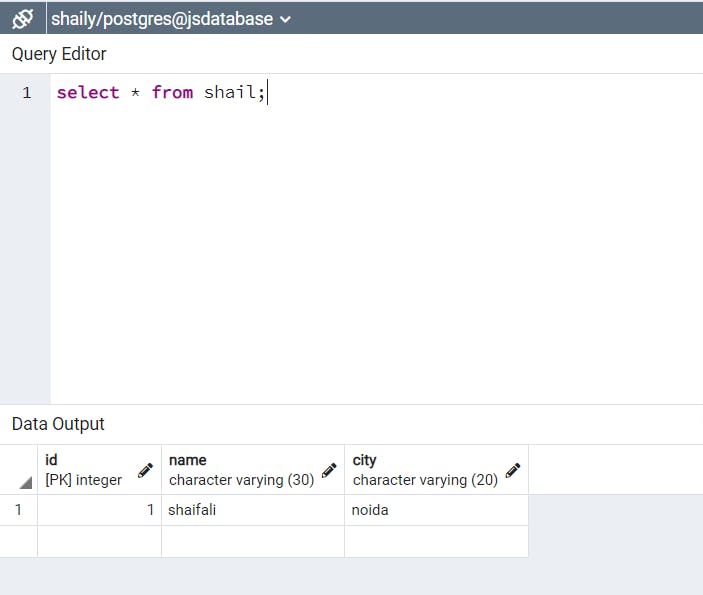
Created one more table with different data.
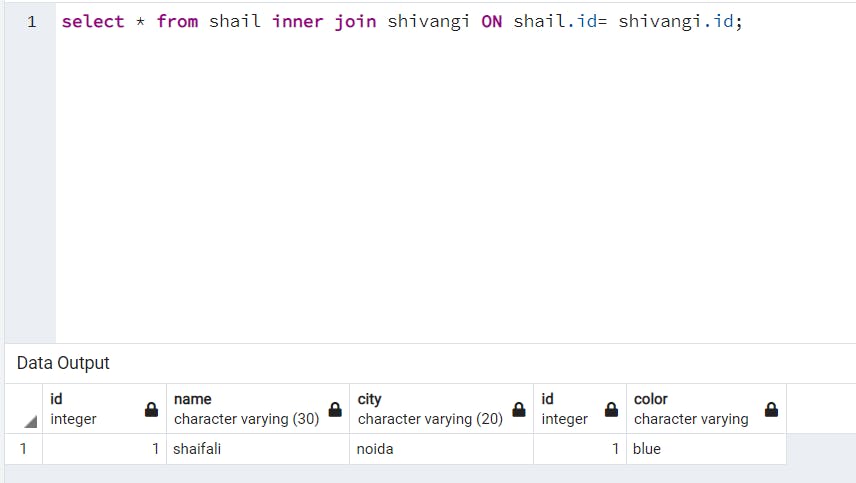
INNER JOIN
CROSS JOIN
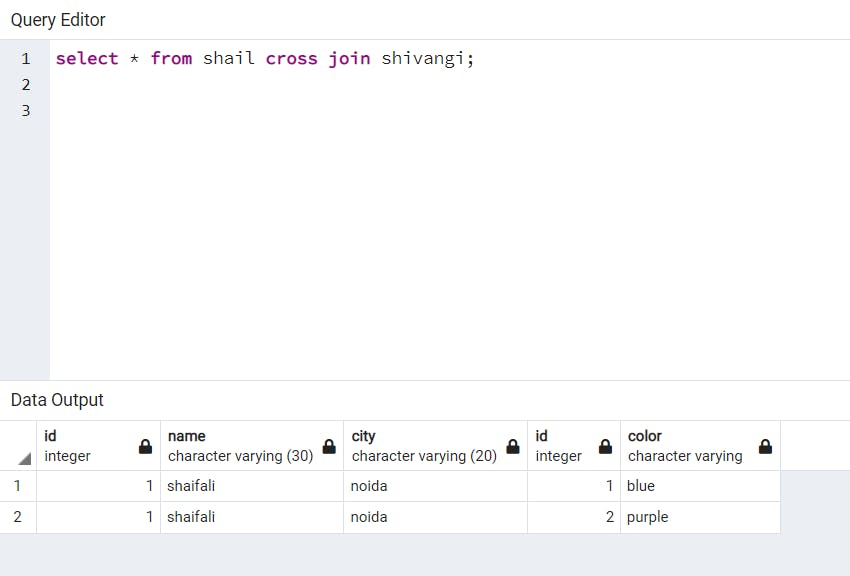
RIGHT OUTER JOIN
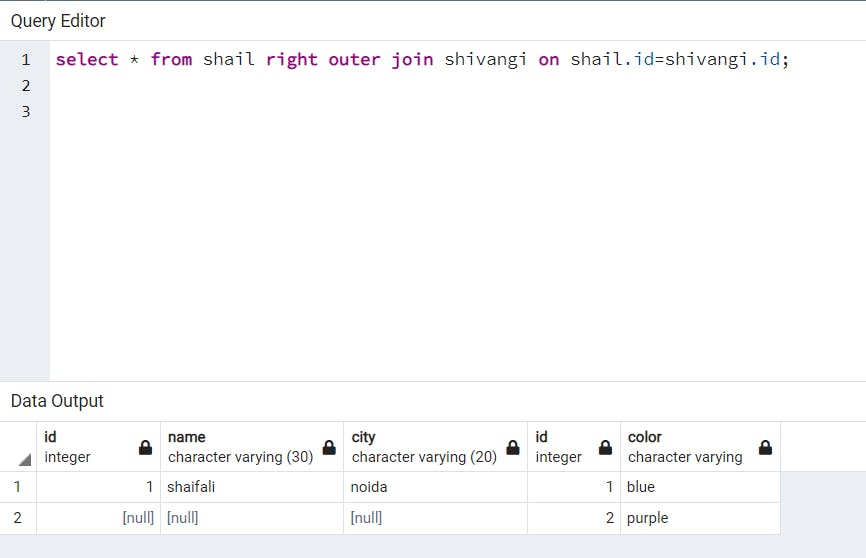
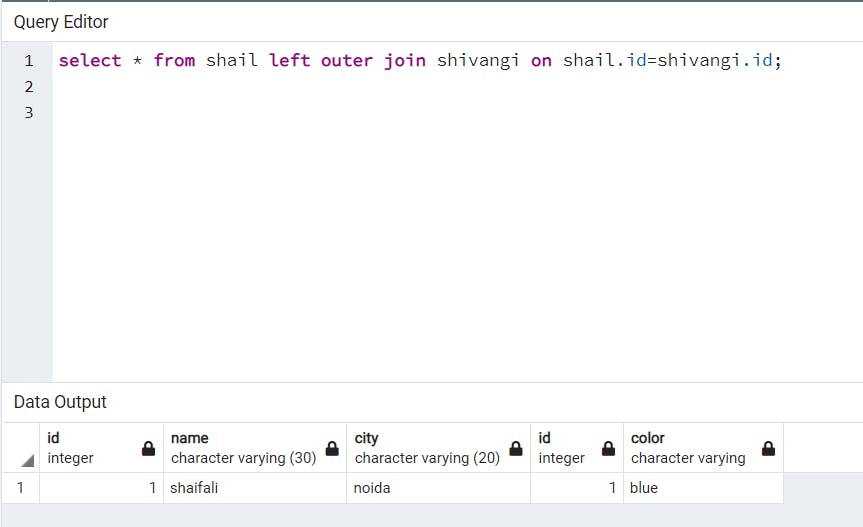
LEFT OUTER JOIN
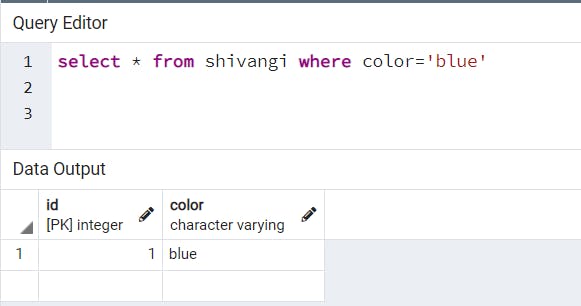
WHERE Condition.
UPDATE TABLE
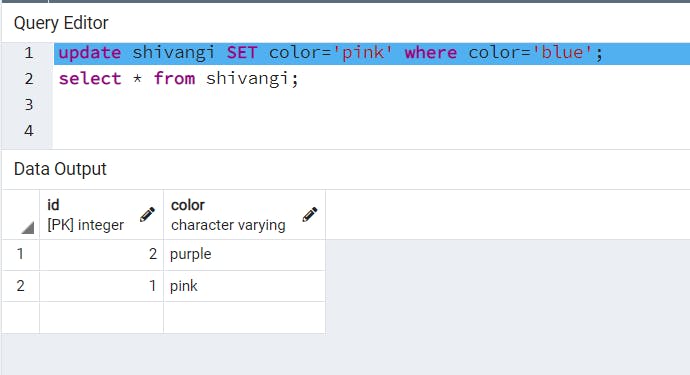
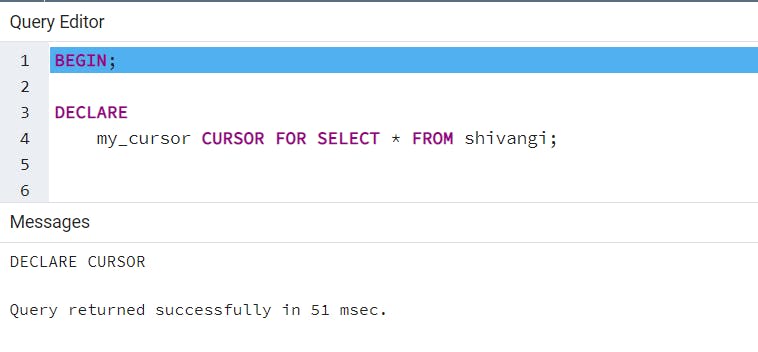
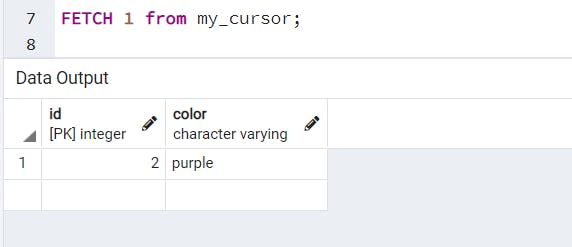
A Cursor in PostgreSQL is used to process large tables. Suppose a table has 10 million or billion rows. While performing a SELECT operation on the table it will take some time to process the result and most likely give an “out of memory” error and the program will be terminated.
A Cursor can only be declared inside a transaction. The cursor does not calculate the data but only prepares the query so that your data can be created when FETCH is called. In the end, simply commit the transaction.
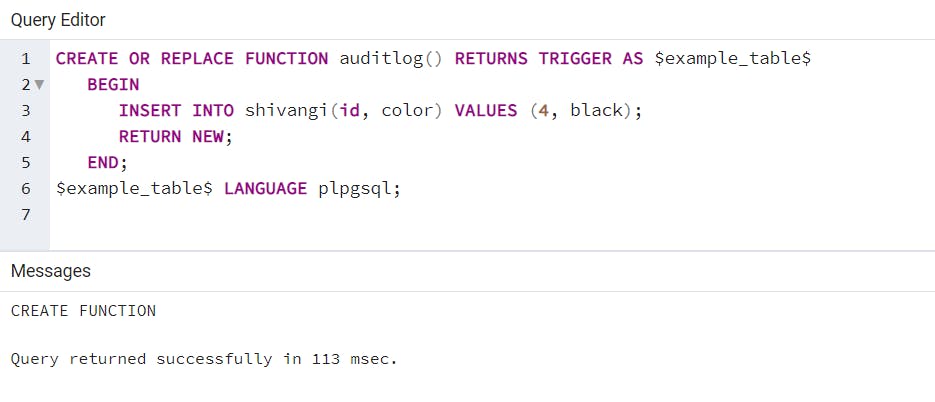
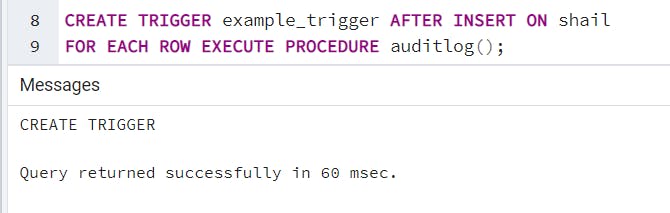
A PostgreSQL Trigger is a function invoked automatically whenever an event associated with a table occurs. An event could be any of the following: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE or TRUNCATE.
A trigger is a special user-defined function associated with a table. To create a new trigger, you must define a trigger function first, and then bind this trigger function to a table. The difference between a trigger and a user-defined function is that a trigger is automatically invoked when an event occurs.
PostgreSQL provides two main types of triggers:
*- Row level-triggers
- Statement-level triggers*

Andrew Baisden
👨💻 Software Developer 📝 Tech Writer LogRocket @freeCodeCamp All things tech and programming 💻
Jun 26, 2022
PostgreSQL is what got me excited to use SQL again after so many years. Quality article by the way shaifali agarwal.
shaifali agarwal
Jun 26, 2022
Thankyou