What is IoT? Internet of Things
Introduction to IoT ( internet of things )
INTRODUCTION: What is the Internet of Things? (IoT)
It’s a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.
These things can be a wide variety of devices such as automobiles with sensors, electric devices with sensors, mechanical or any object with the device that capable of sending/receiving data to the internet.
There’s a lot of noise at the moment about the Internet of Things (or IoT) and its impact on everything from the way we travel and do our shopping, the way manufacturers keep track of inventory. In the very short distant future, hundreds of millions, then billions, of individuals with billions may be more smart devices will stretch the boundaries of the current system.
It has the potential to change the way we work, learn, entertain and innovate. Product with smart access and wireless connectivity are more common than they were five years ago.
It’s a series of technology.
Worldwide technology spending on the Internet of Things to reach $1.2 T in 2022(From IDC) It is not only responsible for sensing things and send data to the network but also perform actions. Things can start to share their experience with other things.
THINGS (can)
Sense + Communicate
Example:
Order Chemical for manufacturing unit automatically Problem with manually - Keeping watch manually by a human and may require a chain of communication to order.
Solution - Smart Chemical storage tank It can sense chemical storage and trigger an order email to a vendor when it reaches to the specific level.
USE CASES
Smart Metering
Smart Water supply in the town
Smart House
Smart Lock
Smart Air Conditioner
- Smart City
- Garbage collector
- Water supply system to control remotely without human interference
- Connected Vehicles
- Connected Cars with sensing ability
- Monitoring tools/objects/product for better productivity
- Manufacturing unit with machinery
- Security system
ADVANTAGES
Communication
- Encourages communication between devices.
- Physical devices are able to stay connected and hence the total transparency is available with lesser inefficiencies and greater quality.
- Increase Business Opportunities
- Applicable to all vertical market
- Opens the door for new business opportunities in all industries.
- IoT-driven innovations build strong business cases, reduce time to market and increase the return of investments.
- Potential to transform the businesses approach/model
- Improve tracking of assets(machinery, tools, equipment, etc) using sensors and connectivity.
- Helps organizations benefit from real-time insights. And take immediate actions.
Efficient Processes
- Being connected with a maximum number of devices to the internet, IoT allows businesses to be smarter with real-time operational insights while reducing operating costs.
- Improved Safety and Security
- Services integrated with sensors and video camera help monitor the workplace to ensure equipment safety and protect against physical threats.
Increase Productivity
- Productivity plays a key role in the profitability of any business.
Cost Saving
The improved process like asset utilization, productivity, real-time insights into important data, and process efficiency can save expenditures. It will reduce the cost of maintenance as well as overall cost.
Minimize Human efforts
TECHNOLOGY STACK
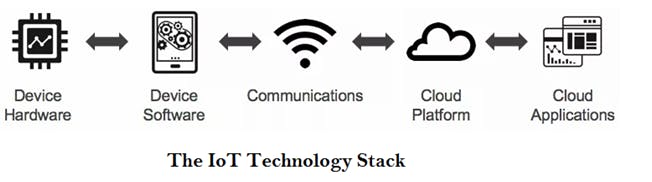
Sensors Temp. and Humidity sensor, Proximity sensor, Pressure sensor, Smoke, Gas and Alcohol Sensor etc. Computing
Microcontrollers like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, NodeMcu Network Access
Internet access through Ethernet or Wi-Fi module Protocols :
Rest API, Message Queuing Telemetry Transport(MQTT) etc.
Cloud/ Server
Azure, Amazon etc.
UI - Using web technologies like HTML, JS etc.
Note The Diagram of IoT is not limited to the above.
Technical Challenges
- Wireless communication in the remote area
- Power Supply
- Security
- Complexity with Series of Technology
- Software Complexity
